Difference between revisions of "Signet ring cell carcinoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = Signet ring cell carcinoma - very high mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
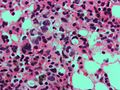
| Caption = Signet ring cell carcinoma. [[H&E stain]] | |||
| Micro = ovoid cells with abundant cytoplasm and a peripheral crescentic hyperchromatic nucleus | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = [[serous fat atrophy]], benign histiocytes ([[mucocele]], [[xanthoma]]) | |||
| Stains = [[mucicarmine stain]], [[PAS stain]] | |||
| IHC = pankeratin +ve, CD68 -ve | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[stomach]], [[breast]], many others | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
}} | |||
{{ Infobox external links | {{ Infobox external links | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | | Name = {{PAGENAME}} | ||
Revision as of 00:11, 9 July 2013
| Signet ring cell carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 Signet ring cell carcinoma. H&E stain | |
|
| |
| LM | ovoid cells with abundant cytoplasm and a peripheral crescentic hyperchromatic nucleus |
| LM DDx | serous fat atrophy, benign histiocytes (mucocele, xanthoma) |
| Stains | mucicarmine stain, PAS stain |
| IHC | pankeratin +ve, CD68 -ve |
| Site | stomach, breast, many others |
|
| |
| Signet ring cell carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| External resources | |
| EHVSC | Eastern Health Virtual Slide Collection (EHVSC) [http://eh-aperio/EditRecord.php?TableName=Slide&Ids%5B%5D=9982 9982 Eastern Health Virtual Slide Collection (EHVSC) 9982] |
| Wikipedia | Signet ring cell carcinoma |
Signet ring cell carcinoma, abbreviated SRCC, is a type of malignant epithelial neoplasm that can arise from a number of places. It is commonly associated with the stomach.
General
- It has been said that there are two types of pathologists... those that have missed SRCCs and those that will miss SRCCs.
Differential diagnosis
It may arise from the:[1]
Microscopic
Features:
- Signet ring cells resemble signet rings.
- They contain a large amount of mucin, which pushes the nucleus to the cell periphery.
- The pool of mucin in a signet ring cell mimics the appearance of the finger hole.
- The nucleus mimics the appearance of the face of the ring in profile.
- Signet ring cells are typically 2-3x the size of a lymphocyte.
- Smaller than the typical adipocyte.
- Often have a crescent-shaped or ovoid nucleus.
- Capillaries sectioned on their lumen have endothelial cells - the nuclei of these are more spindled.
Note:
- SRCs are usually close to friend, i.e. they are adjacent to another SRC.
- This helps differentiate SRCs from capillaries sectioned on their lumen.
- The mucin is often clear on H&E... but maybe eosinophilic.
DDx:
- Serous fat atrophy.[2]
- Mucocele - muciphages may mimic signet ring cells.[3]
- Muciphages = cytoplasm lightly eosinophilic, multivaculated (classic) or finely reticulated.
Images
www:
Stains
- PAS stain +ve.
- Alican blue-PAS stain +ve.
IHC
- AE1/AE3 +ve.
- CK7 +ve.
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://cancerhelp.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/cancer-questions/what-is-a-signet-cell-cancer. Accessed on: 7 March 2012.
- ↑ Clarke, BE.; Brown, DJ.; Xipell, JM. (Jan 1983). "Gelatinous transformation of the bone marrow.". Pathology 15 (1): 85-8. PMID 6222282.
- ↑ De Petris, G.; Lev, R.; Siew, S. (May 1998). "Peritumoral and nodal muciphages.". Am J Surg Pathol 22 (5): 545-9. PMID 9591723.