Difference between revisions of "Pseudomembranous colitis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(redirect) |
(split-out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Pseudomembranous colitis''' an inflammation of the [[colon]] ([[colitis]]) with a characteristic endoscopic/gross appearance. It is closely associated with ''C. difficle'' infectious; however, may be seen in a number of different situations. | |||
==General== | |||
*''Pseudomembranous colitis'' is a histomorphologic description which has a [[DDx]]. In other words, it can be caused by a number of things. | |||
DDx of pseudomembranous colitis:<ref name=Ref_PBoD837-8>{{Ref PBoD|837-8}}</ref> | |||
*[[C. difficile]]. | |||
**Known as ''C. difficile colitis''. | |||
*[[Ischemic colitis]]. | |||
**Volvulus. | |||
*Other infections. | |||
Etiology: | |||
*Anything that causes a severe mucosal injury. | |||
==Gross== | |||
Features:<ref>URL: [http://radiology.uchc.edu/eAtlas/GI/1749.htm http://radiology.uchc.edu/eAtlas/GI/1749.htm]. Accessed on: 22 May 2012.</ref> | |||
*Pseudomembranes: | |||
**Pale yellow (or white) irregular, raised mucosal lesions. | |||
**Early lesions: typical <10 mm. | |||
*Interlesional mucosa often near normal grossly. | |||
===Images=== | |||
*[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:PMC_1.jpg Pseudomembranous colitis - endoscopic image (WP/Samir)]. | |||
<gallery> | |||
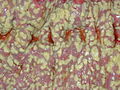
Image:Pseudomembranous_colitis.JPG | Pseudomembranous colitis. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features:<ref name=Ref_PBoD837-8>{{Ref PBoD|837-8}}</ref> | |||
*Heaped necrotic surface epithelium. | |||
**Described as "volanco lesions" - this is what is seen endoscopically. | |||
*[[PMN]]s in lamina propria. | |||
*+/-Capillary fibrin thrombi. | |||
Notes: | |||
*Pseudomembranes arise from the crypts. | |||
*Rarely have (benign) [[signet ring cell]]-like cells.<ref name=pmid12684766>{{Cite journal | last1 = Abdulkader | first1 = I. | last2 = Cameselle-Teijeiro | first2 = J. | last3 = Forteza | first3 = J. | title = Signet-ring cells associated with pseudomembranous colitis. | journal = Virchows Arch | volume = 442 | issue = 4 | pages = 412-4 | month = Apr | year = 2003 | doi = 10.1007/s00428-003-0779-1 | PMID = 12684766 }}</ref> | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Cap polyposis]] - very rare. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
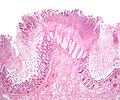
Image:Colonic_pseudomembranes_low_mag.jpg | Pseudomembranes - low mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
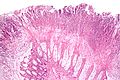
Image:Colonic_pseudomembranes_intermed_mag.jpg | Pseudomembranes - intermed. mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case153.html Pseudomembranous colitis (upmc.edu)]. | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Ischemic colitis]]. | |||
*[[Colon]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Colon]] | |||
Revision as of 01:58, 13 January 2014
Pseudomembranous colitis an inflammation of the colon (colitis) with a characteristic endoscopic/gross appearance. It is closely associated with C. difficle infectious; however, may be seen in a number of different situations.
General
- Pseudomembranous colitis is a histomorphologic description which has a DDx. In other words, it can be caused by a number of things.
DDx of pseudomembranous colitis:[1]
- C. difficile.
- Known as C. difficile colitis.
- Ischemic colitis.
- Volvulus.
- Other infections.
Etiology:
- Anything that causes a severe mucosal injury.
Gross
Features:[2]
- Pseudomembranes:
- Pale yellow (or white) irregular, raised mucosal lesions.
- Early lesions: typical <10 mm.
- Interlesional mucosa often near normal grossly.
Images
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Heaped necrotic surface epithelium.
- Described as "volanco lesions" - this is what is seen endoscopically.
- PMNs in lamina propria.
- +/-Capillary fibrin thrombi.
Notes:
- Pseudomembranes arise from the crypts.
- Rarely have (benign) signet ring cell-like cells.[3]
DDx:
- Cap polyposis - very rare.
Images
www:
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 837-8. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ URL: http://radiology.uchc.edu/eAtlas/GI/1749.htm. Accessed on: 22 May 2012.
- ↑ Abdulkader, I.; Cameselle-Teijeiro, J.; Forteza, J. (Apr 2003). "Signet-ring cells associated with pseudomembranous colitis.". Virchows Arch 442 (4): 412-4. doi:10.1007/s00428-003-0779-1. PMID 12684766.