Difference between revisions of "Mast cell"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
*[[Neurofibroma]]. | *[[Neurofibroma]]. | ||
*[[Melanocytic nevi]].<ref name=pmid8432898>{{Cite journal | last1 = Carr | first1 = NJ. | last2 = Warren | first2 = AY. | title = Mast cell numbers in melanocytic naevi and cutaneous neurofibromas. | journal = J Clin Pathol | volume = 46 | issue = 1 | pages = 86-7 | month = Jan | year = 1993 | doi = | PMID = 8432898 }}</ref> | *[[Melanocytic nevi]].<ref name=pmid8432898>{{Cite journal | last1 = Carr | first1 = NJ. | last2 = Warren | first2 = AY. | title = Mast cell numbers in melanocytic naevi and cutaneous neurofibromas. | journal = J Clin Pathol | volume = 46 | issue = 1 | pages = 86-7 | month = Jan | year = 1993 | doi = | PMID = 8432898 }}</ref> | ||
*[[Succinate dehydrogenase-deficient renal cell carcinoma]]. | *[[Succinate dehydrogenase-deficient renal cell carcinoma]].<ref name=pmid25034258>{{Cite journal | last1 = Williamson | first1 = SR. | last2 = Eble | first2 = JN. | last3 = Amin | first3 = MB. | last4 = Gupta | first4 = NS. | last5 = Smith | first5 = SC. | last6 = Sholl | first6 = LM. | last7 = Montironi | first7 = R. | last8 = Hirsch | first8 = MS. | last9 = Hornick | first9 = JL. | title = Succinate dehydrogenase-deficient renal cell carcinoma: detailed characterization of 11 tumors defining a unique subtype of renal cell carcinoma. | journal = Mod Pathol | volume = | issue = | pages = | month = Jul | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1038/modpathol.2014.86 | PMID = 25034258 }}</ref> | ||
==Stains== | ==Stains== | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
*CD117 +ve. | *CD117 +ve.<ref name=pmid25038510>{{Cite journal | last1 = Schmetzer | first1 = O. | last2 = Valentin | first2 = P. | last3 = Smorodchenko | first3 = A. | last4 = Domenis | first4 = R. | last5 = Gri | first5 = G. | last6 = Siebenhaar | first6 = F. | last7 = Metz | first7 = M. | last8 = Maurer | first8 = M. | title = A novel method to generate and culture human mast cells: Peripheral CD34+ stem cell-derived mast cells (PSCMCs). | journal = J Immunol Methods | volume = | issue = | pages = | month = Jul | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1016/j.jim.2014.07.003 | PMID = 25038510 }}</ref> | ||
*CD34 +ve.<ref name=pmid22119830>{{Cite journal | last1 = Duşe | first1 = AO. | last2 = Ceauşu | first2 = RA. | last3 = Mezei | first3 = T. | last4 = Cîmpean | first4 = AM. | last5 = Gaje | first5 = P. | last6 = Ioniţă | first6 = H. | last7 = Jung | first7 = I. | title = Mast cells contribute to the angiogenesis in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. An immunohistochemical study based on the relationship with microvessel density. | journal = Rom J Morphol Embryol | volume = 52 | issue = 3 Suppl | pages = 1091-6 | month = | year = 2011 | doi = | PMID = 22119830 }}</ref>{{fact}} | *CD34 +ve.<ref name=pmid22119830>{{Cite journal | last1 = Duşe | first1 = AO. | last2 = Ceauşu | first2 = RA. | last3 = Mezei | first3 = T. | last4 = Cîmpean | first4 = AM. | last5 = Gaje | first5 = P. | last6 = Ioniţă | first6 = H. | last7 = Jung | first7 = I. | title = Mast cells contribute to the angiogenesis in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. An immunohistochemical study based on the relationship with microvessel density. | journal = Rom J Morphol Embryol | volume = 52 | issue = 3 Suppl | pages = 1091-6 | month = | year = 2011 | doi = | PMID = 22119830 }}</ref>{{fact}} | ||
Latest revision as of 19:05, 27 October 2014
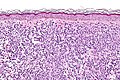
The mast cell is an uncommonly cell that occasionally causes problems.
Microscopic
Features:
- Ovoid/round cell with moderate amount of gray granular cytoplasm.
- Nuclear ovoid/round.
- No obvious nucleolus.
- May be more abundant around blood vessels.
Notes:
- Lymphocyte vs. mast cell:
- Lymphocytes = round; mast cells = ovoid.
Images
www:
- Mastocytosis - low res. (jameswpattersonmd.com).
- Mastocytosis - bone marrow - several images (upmc.edu).
Diseases
- Mastocytosis.
- Urticaria pigmentosa.
- Asthma.[1]
Conditions associated with the presence of mast cells
Stains
- Giemsa stain.
- Tyrosinase.[4] (???)
IHC
- CD117 +ve.[5]
- CD34 +ve.[6][citation needed]
References
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 370-2. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ Carr, NJ.; Warren, AY. (Jan 1993). "Mast cell numbers in melanocytic naevi and cutaneous neurofibromas.". J Clin Pathol 46 (1): 86-7. PMID 8432898.
- ↑ Williamson, SR.; Eble, JN.; Amin, MB.; Gupta, NS.; Smith, SC.; Sholl, LM.; Montironi, R.; Hirsch, MS. et al. (Jul 2014). "Succinate dehydrogenase-deficient renal cell carcinoma: detailed characterization of 11 tumors defining a unique subtype of renal cell carcinoma.". Mod Pathol. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2014.86. PMID 25034258.
- ↑ URL: http://www.nature.com/jid/journal/v53/n1/full/jid1969105a.html. Accessed on: 20 December 2011.
- ↑ Schmetzer, O.; Valentin, P.; Smorodchenko, A.; Domenis, R.; Gri, G.; Siebenhaar, F.; Metz, M.; Maurer, M. (Jul 2014). "A novel method to generate and culture human mast cells: Peripheral CD34+ stem cell-derived mast cells (PSCMCs).". J Immunol Methods. doi:10.1016/j.jim.2014.07.003. PMID 25038510.
- ↑ Duşe, AO.; Ceauşu, RA.; Mezei, T.; Cîmpean, AM.; Gaje, P.; Ioniţă, H.; Jung, I. (2011). "Mast cells contribute to the angiogenesis in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. An immunohistochemical study based on the relationship with microvessel density.". Rom J Morphol Embryol 52 (3 Suppl): 1091-6. PMID 22119830.