Difference between revisions of "Diabetes mellitus"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
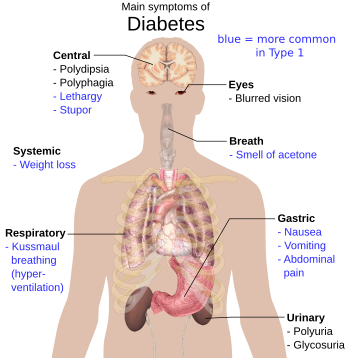
'''Diabetes mellitus''', often | [[Image:Main symptoms of diabetes.svg|thumb|right|350px|The manifestations of diabetes mellitus from a clinical perspective. (WC/Mikael Häggström)]] | ||
'''Diabetes mellitus''', often just '''[[diabetes]]''', is a common affliction that is increasing with the expanding waistlines. It is commonly abbreviated '''DM'''. | |||
=General= | =General= | ||
*Major cardiovascular risk factor. | *Major cardiovascular risk factor. | ||
*Many subtypes. | *Many subtypes. | ||
**Most common type 2 | **Most common: DM type 2 -- strongly associated with [[obesity]]. | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 14: | ||
==Classic complications== | ==Classic complications== | ||
Family medicine - mnemonic ''HELP'': | Family medicine - mnemonic ''HELP'': | ||
*H - HbA1c, | *H - HbA1c, [[hypertension]]. | ||
*E - eye. | *E - [[eye]]. | ||
*L - lipids. | *L - lipids. | ||
*P - podiatry, proteinuria, Pneumococcus vaccine. | *P - podiatry, proteinuria, Pneumococcus vaccine. | ||
| Line 20: | Line 21: | ||
==Emergency room presentations== | ==Emergency room presentations== | ||
*[[Ketoacidosis]] - DM type 1. | *[[Ketoacidosis]] - DM type 1. | ||
*HONK - DM type 2. | *Hyperosmotic non-ketotic (HONK) coma - DM type 2. | ||
=Subspecialty specific findings= | =Subspecialty specific findings= | ||
| Line 33: | Line 34: | ||
*[[Pancreas|Pancreatic]] [[amyloid]] deposition - in DM type 2.<ref>URL: [http://www.umm.edu/altmed/articles/amyloidosis-000007.htm http://www.umm.edu/altmed/articles/amyloidosis-000007.htm]. Accessed on: 23 October 2010.</ref> | *[[Pancreas|Pancreatic]] [[amyloid]] deposition - in DM type 2.<ref>URL: [http://www.umm.edu/altmed/articles/amyloidosis-000007.htm http://www.umm.edu/altmed/articles/amyloidosis-000007.htm]. Accessed on: 23 October 2010.</ref> | ||
*Centrilobular [[macrovescicular steatosis]] of the [[liver]]. | *Centrilobular [[macrovescicular steatosis]] of the [[liver]]. | ||
*[[Pancreatic islet cell hyperplasia]] - in the fetus of a mother with diabetes. | |||
==Breast pathology== | ==Breast pathology== | ||
| Line 42: | Line 44: | ||
==Placental pathology== | ==Placental pathology== | ||
*[[Placentomegaly]]. | |||
*[[Placental villous immaturity]]. | *[[Placental villous immaturity]]. | ||
*[[Chorangiosis]].<ref name=pmid20594143>{{cite journal |author=Amer HZ, Heller DS |title=Chorangioma and related vascular lesions of the placenta--a review |journal=Fetal Pediatr Pathol |volume=29 |issue=4 |pages=199–206 |year=2010 |pmid=20594143 |doi=10.3109/15513815.2010.487009 |url=}}</ref> | *[[Chorangiosis]].<ref name=pmid20594143>{{cite journal |author=Amer HZ, Heller DS |title=Chorangioma and related vascular lesions of the placenta--a review |journal=Fetal Pediatr Pathol |volume=29 |issue=4 |pages=199–206 |year=2010 |pmid=20594143 |doi=10.3109/15513815.2010.487009 |url=}}</ref> | ||
*Two-vessel cord.<ref name=pmid7997408>{{cite journal |author=Lilja M |title=Infants with single umbilical artery studied in a national registry. 3: A case control study of risk factors |journal=Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol |volume=8 |issue=3 |pages=325–33 |year=1994 |month=July |pmid=7997408 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | *[[Two-vessel cord]].<ref name=pmid7997408>{{cite journal |author=Lilja M |title=Infants with single umbilical artery studied in a national registry. 3: A case control study of risk factors |journal=Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol |volume=8 |issue=3 |pages=325–33 |year=1994 |month=July |pmid=7997408 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
==Cardiovascular pathology== | ==Cardiovascular pathology== | ||
*[[Atherosclerosis]]. | *[[Atherosclerosis]]. | ||
**[[Coronary artery disease]]. | |||
***[[Myocardial infarction]]. | |||
***[[Congestive heart failure]]. | |||
**[[Stroke]]. | |||
**[[Peripheral vascular disease]]. | |||
*[[Arterial hyaline]] - in both afferent and efferent arteriole of the [[kidney]]. | *[[Arterial hyaline]] - in both afferent and efferent arteriole of the [[kidney]]. | ||
==Neuropathology== | ==Neuropathology== | ||
*Idiopathic inflammatory myositis.<ref name=pmid20536597>{{cite journal |author=Limaye VS, Lester S, Blumbergs P, Roberts-Thomson PJ |title=Idiopathic inflammatory myositis is associated with a high incidence of hypertension and diabetes mellitus |journal=Int J Rheum Dis |volume=13 |issue=2 |pages=132–7 |year=2010 |month=May |pmid=20536597 |doi=10.1111/j.1756-185X.2010.01470.x |url=}}</ref> | *Idiopathic inflammatory myositis.<ref name=pmid20536597>{{cite journal |author=Limaye VS, Lester S, Blumbergs P, Roberts-Thomson PJ |title=Idiopathic inflammatory myositis is associated with a high incidence of hypertension and diabetes mellitus |journal=Int J Rheum Dis |volume=13 |issue=2 |pages=132–7 |year=2010 |month=May |pmid=20536597 |doi=10.1111/j.1756-185X.2010.01470.x |url=}}</ref> | ||
==Forensic pathology== | |||
*Diabetic coma (preceding death) at [[autopsy]] - may be demonstrated with an elevated glucose in the vitreous fluid.<ref name=pmid19167848>{{Cite journal | last1 = Zilg | first1 = B. | last2 = Alkass | first2 = K. | last3 = Berg | first3 = S. | last4 = Druid | first4 = H. | title = Postmortem identification of hyperglycemia. | journal = Forensic Sci Int | volume = 185 | issue = 1-3 | pages = 89-95 | month = Mar | year = 2009 | doi = 10.1016/j.forsciint.2008.12.017 | PMID = 19167848 }}</ref> | |||
=References= | =References= | ||
Latest revision as of 06:02, 2 January 2016
Diabetes mellitus, often just diabetes, is a common affliction that is increasing with the expanding waistlines. It is commonly abbreviated DM.
General
- Major cardiovascular risk factor.
- Many subtypes.
- Most common: DM type 2 -- strongly associated with obesity.
Diagnosis
Based on biochemistry, specifically:
- Fasting blood glucose >=7.0 mmol/L.
- Two-hour glucose tolerance test >=11.1 mmol/L.
Classic complications
Family medicine - mnemonic HELP:
- H - HbA1c, hypertension.
- E - eye.
- L - lipids.
- P - podiatry, proteinuria, Pneumococcus vaccine.
Emergency room presentations
- Ketoacidosis - DM type 1.
- Hyperosmotic non-ketotic (HONK) coma - DM type 2.
Subspecialty specific findings
Dermatopathology
Other:
Gastrointestinal pathology
- Microscopic colitis - generally assoc. with autoimmune disorders.
- Pancreatic amyloid deposition - in DM type 2.[1]
- Centrilobular macrovescicular steatosis of the liver.
- Pancreatic islet cell hyperplasia - in the fetus of a mother with diabetes.
Breast pathology
Genitourinary pathology
Placental pathology
Cardiovascular pathology
- Atherosclerosis.
- Arterial hyaline - in both afferent and efferent arteriole of the kidney.
Neuropathology
- Idiopathic inflammatory myositis.[4]
Forensic pathology
- Diabetic coma (preceding death) at autopsy - may be demonstrated with an elevated glucose in the vitreous fluid.[5]
References
- ↑ URL: http://www.umm.edu/altmed/articles/amyloidosis-000007.htm. Accessed on: 23 October 2010.
- ↑ Amer HZ, Heller DS (2010). "Chorangioma and related vascular lesions of the placenta--a review". Fetal Pediatr Pathol 29 (4): 199–206. doi:10.3109/15513815.2010.487009. PMID 20594143.
- ↑ Lilja M (July 1994). "Infants with single umbilical artery studied in a national registry. 3: A case control study of risk factors". Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 8 (3): 325–33. PMID 7997408.
- ↑ Limaye VS, Lester S, Blumbergs P, Roberts-Thomson PJ (May 2010). "Idiopathic inflammatory myositis is associated with a high incidence of hypertension and diabetes mellitus". Int J Rheum Dis 13 (2): 132–7. doi:10.1111/j.1756-185X.2010.01470.x. PMID 20536597.
- ↑ Zilg, B.; Alkass, K.; Berg, S.; Druid, H. (Mar 2009). "Postmortem identification of hyperglycemia.". Forensic Sci Int 185 (1-3): 89-95. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2008.12.017. PMID 19167848.