Difference between revisions of "Medial calcific sclerosis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+images) |
|||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
| Micro = calcifications of the tunica media | | Micro = calcifications of the tunica media | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = | ||
| LMDDx = | | LMDDx = [[atherosclerosis]] | ||
| Stains = | | Stains = | ||
| IHC = | | IHC = | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
| Grossing = | | Grossing = | ||
| Staging = | | Staging = | ||
| Site = | | Site = [[blood vessels]] - arteries | ||
| Assdx = | | Assdx = | ||
| Syndromes = | | Syndromes = | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
Note: | Note: | ||
*Lumen unaffected. | *Lumen unaffected. | ||
DDx: | |||
*[[Atherosclerosis]] (severe) - intimal hyperplasia, calcifications typically in tunica intima. | |||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
Revision as of 03:49, 7 March 2016
| Medial calcific sclerosis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
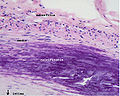
 Medial calcific sclerosis. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | Moenckeberg medial calcific sclerosis, calcific medial sclerosis of Monckeberg, Mönckeberg's arteriosclerosis (also written Monckeberg's arteriosclerosis) |
|
| |
| LM | calcifications of the tunica media |
| LM DDx | atherosclerosis |
| Site | blood vessels - arteries |
|
| |
| Prognosis | good |
| Treatment | (nothing) |
Medial calcific sclerosis is a type of arteriosclerosis that has no significant clinical impact.
It is also known as Moenckeberg medial calcific sclerosis, calcific medial sclerosis of Monckeberg, and Mönckeberg's arteriosclerosis (also written Monckeberg's arteriosclerosis).
General
- Usually of no clinical consequence.
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Medial calcification (purple irregular stuff on H&E -- calcium phosphate).
Note:
- Lumen unaffected.
DDx:
- Atherosclerosis (severe) - intimal hyperplasia, calcifications typically in tunica intima.
Images
www:
Sign out
RIGHT LEG, BELOW KNEE AMPUTATION: - MINIMAL-TO-MILD LARGE VESSEL ATHEROSCLEROSIS, SEE COMMENT. - MEDIAL CALCIFIC SCLEROSIS. - SKIN WITH DERMAL FIBROSIS. COMMENT: The sections may not be representative of disease in the distal vascular bed.
See also
References
- ↑ Klatt, Edward C. (2006). Robbins and Cotran Atlas of Pathology (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 7. ISBN 978-1416002741.