Difference between revisions of "Liver pathology"
(+images) |
m (H&E image) |
||
| (31 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
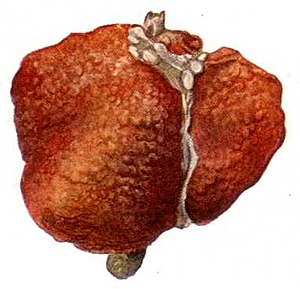
[[Image:Wątroba marska (Ultima Thule).jpg|thumb|right|Drawing of a [[cirrhosis|cirrhotic]] liver. (WC)]] | |||
The '''liver''' is an organ [[pathologist]]s are seeing less of, as [[radiologist]]s (with multimodal imaging and triphasic CT scans) are pretty good at sorting-out many types of liver lesions. | The '''liver''' is an organ [[pathologist]]s are seeing less of, as [[radiologist]]s (with multimodal imaging and triphasic CT scans) are pretty good at sorting-out many types of liver lesions. | ||
This article is an introduction to liver pathology. Liver neoplasms are dealt with in the ''[[liver neoplasms]]'' article. Medical liver diseases (e.g. viral hepatitis) is dealt with in the ''[[medical liver disease]]'' article. | This article is an introduction to liver pathology. Liver neoplasms are dealt with in the ''[[liver neoplasms]]'' article. Medical liver diseases (e.g. viral hepatitis) is dealt with in the ''[[medical liver disease]]'' article. | ||
=Review of liver blood work= | =Review of liver blood work= | ||
*This is covered in the ''[[Medical_liver_disease#Review_of_liver_blood_work|medical liver disease]]'' article. | |||
* | |||
=Normal liver= | =Normal liver= | ||
| Line 121: | Line 35: | ||
**Bile duct - round, has a lumen - approximately the size of the artery. | **Bile duct - round, has a lumen - approximately the size of the artery. | ||
***Cuboidal epithelium, central nucleus, lightly basophilic cytoplasm. | ***Cuboidal epithelium, central nucleus, lightly basophilic cytoplasm. | ||
***IHC: CK7 +ve. | ***IHC: [[CK7]] +ve. | ||
***Irregular bile ducts without a lumen are called ''bile ductules''; ''ductule'' implies a pathologic process. | ***Irregular bile ducts without a lumen are called ''bile ductules''; ''ductule'' implies a pathologic process. | ||
*Lobule - hepatocytes. | *Lobule - hepatocytes. | ||
| Line 192: | Line 106: | ||
Common IHC:<ref name=ap27may2009>Pollet, A. 27 May 2009.</ref> | Common IHC:<ref name=ap27may2009>Pollet, A. 27 May 2009.</ref> | ||
*CK7 - bile ducts, and bile ductules +ve. | *[[CK7]] - bile ducts, and bile ductules +ve. | ||
*CD34 - should be -ve in normal liver. | *CD34 - should be -ve in normal liver. | ||
**CD34 marks endothelial cells - these are not present in a healthy liver lobule. | **CD34 marks endothelial cells - these are not present in a healthy liver lobule. | ||
| Line 198: | Line 112: | ||
=Liver biopsy= | =Liver biopsy= | ||
==Medical liver biopsy adequacy== | ==Medical liver biopsy adequacy== | ||
*This is covered in the ''[[Medical_liver_disease#Medical_liver_biopsy_adequacy|medical liver disease]]'' article. | |||
* | |||
==Reporting== | ==Reporting== | ||
{{Main|Pathology reports}} | {{Main|Pathology reports}} | ||
*This is covered in the ''[[Medical_liver_disease#Reporting|medical liver disease]]'' article. | |||
* | |||
=Liver injury terms/histologic findings= | =Liver injury terms/histologic findings= | ||
| Line 246: | Line 146: | ||
Image:Von_Meyenburg_complex_low_mag.jpg | Von Meyenburg complex - bile duct hamartoma (WC) | Image:Von_Meyenburg_complex_low_mag.jpg | Von Meyenburg complex - bile duct hamartoma (WC) | ||
Image:Bile_duct_hamartoma_intermed_mag.jpg | Bile duct hamartoma - intermed. mag. (WC) | Image:Bile_duct_hamartoma_intermed_mag.jpg | Bile duct hamartoma - intermed. mag. (WC) | ||
Image:Von_Meyenburg_complex_liver.jpg | Von Meyenburg complex / bile duct hamartoma (WC) | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
www: | www: | ||
| Line 260: | Line 161: | ||
===Ballooning degeneration=== | ===Ballooning degeneration=== | ||
{{Main|Ballooning degeneration}} | |||
===Ground glass hepatocytes=== | ===Ground glass hepatocytes=== | ||
{{Main|Ground glass hepatocyte}} | |||
===Mallory bodies=== | ===Mallory bodies=== | ||
| Line 411: | Line 263: | ||
====Interface hepatitis==== | ====Interface hepatitis==== | ||
*May be referred to as ''piecemeal necrosis''.<ref name=aop>Atlas of Pathology. URL: [http://www.pathologyatlas.ro/viral-chronic-moderate-hepatitis.php http://www.pathologyatlas.ro/viral-chronic-moderate-hepatitis.php]. Accessed on: September 1, 2009.</ref> | *May be referred to as ''piecemeal necrosis''.<ref name=aop>Atlas of Pathology. URL: [http://www.pathologyatlas.ro/viral-chronic-moderate-hepatitis.php http://www.pathologyatlas.ro/viral-chronic-moderate-hepatitis.php]. Accessed on: September 1, 2009.</ref> | ||
*Non-specific finding, i.e. seen in several conditions - e.g. viral hepatitis, autoimmune hepatitis. | *Non-specific finding, i.e. seen in several conditions - e.g. [[viral hepatitis]], [[autoimmune hepatitis]]. | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
*Inflammation disrupts the "limiting plate", i.e. there is disruption of the hepatocytes that separate the portal tracts from the lobules. | *Inflammation disrupts the "limiting plate", i.e. there is disruption of the hepatocytes that separate the portal tracts from the lobules. | ||
=====Images===== | |||
*[http://www.pathologyatlas.ro/viral-chronic-moderate-hepatitis.php Interface hepatitis (pathologyatlas.ro)] | <gallery> | ||
Image: Interface hepatitis -- high mag.jpg | IH (mild) - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Interface hepatitis -- very high mag.jpg | IH (mild) - very high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.pathologyatlas.ro/viral-chronic-moderate-hepatitis.php Interface hepatitis (pathologyatlas.ro)]. | |||
*[http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v20/n1s/fig_tab/3800693f1.html#figure-title Interface hepatitis (nature.com)].<ref name=pmid17486049>{{cite journal |author=Theise ND |title=Liver biopsy assessment in chronic viral hepatitis: a personal, practical approach |journal=Mod. Pathol. |volume=20 Suppl 1 |issue= |pages=S3-14 |year=2007 |month=February |pmid=17486049 |doi=10.1038/modpathol.3800693 |url=http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v20/n1s/full/3800693a.html}}</ref> | |||
===Liver fibrosis=== | ===Liver fibrosis=== | ||
| Line 449: | Line 307: | ||
===Cirrhosis=== | ===Cirrhosis=== | ||
{{Main|Cirrhosis}} | |||
===Steatosis=== | |||
{{Main|Steatosis}} | |||
===Cholestasis=== | ===Cholestasis=== | ||
{{Main|Cholestasis}} | |||
{ | |||
=Diseases= | =Diseases= | ||
| Line 643: | Line 328: | ||
*[[Hydatid cyst]]. | *[[Hydatid cyst]]. | ||
**Images: [http://pathmicro.med.sc.edu/parasitology/hydatid-hist1.jpg Hydatid cyst (med.sc.edu)] [http://www.atlas.or.kr/atlas/include/viewImg.html?uid=645 Hydatid cyst (atlas.or.kr)] [http://cal.vet.upenn.edu/projects/paraav/images/lab7-14.jpg] | **Images: [http://pathmicro.med.sc.edu/parasitology/hydatid-hist1.jpg Hydatid cyst (med.sc.edu)] [http://www.atlas.or.kr/atlas/include/viewImg.html?uid=645 Hydatid cyst (atlas.or.kr)] [http://cal.vet.upenn.edu/projects/paraav/images/lab7-14.jpg] | ||
*[[ | *[[Liver hemangioma]]. | ||
**Images: [http://www.pathguy.com/lectures/cavernous_hemangioma.jpg Hemangioma (pathguy.com)] [http://www.ikp.unibe.ch/lab2/Hemang.jpg Hemangioma (ikp.unibe.ch)] | **Images: [http://www.pathguy.com/lectures/cavernous_hemangioma.jpg Hemangioma (pathguy.com)] [http://www.ikp.unibe.ch/lab2/Hemang.jpg Hemangioma (ikp.unibe.ch)] | ||
*[[Hepatic adenoma]]. | *[[Hepatic adenoma]]. | ||
Latest revision as of 21:29, 23 June 2018
The liver is an organ pathologists are seeing less of, as radiologists (with multimodal imaging and triphasic CT scans) are pretty good at sorting-out many types of liver lesions.
This article is an introduction to liver pathology. Liver neoplasms are dealt with in the liver neoplasms article. Medical liver diseases (e.g. viral hepatitis) is dealt with in the medical liver disease article.
Review of liver blood work
- This is covered in the medical liver disease article.
Normal liver
Liver anatomy
The liver is divided into eight (Couinaud) segments:
- Segment I = caudate lobe.
- Segments II to VIII = clockwise from left upper lobe to left upper quadrant of the liver to the right of the inferior vena cava.
- Segment IV is divided into: IVa (superior) and IVb (inferior).
Image:
Liver histology
Liver has a dual blood supply:
- Portal vein.
- Hepatic artery.
- The arterial flow is increased in cirrhosis.
Blood most likely flows through several hepatic lobules on one transit through the liver[1] and likely has the following arrangements of hepatic sinusoids:[2]
- Direct sinusoids - short flow path, no detours.
- Branching sinusoids - direct connection between inlet and outlet; however, have branch points for detours.
- Interconnecting sinusoids - connect branching sinusoids.
Structural approach
Examine:
- Portal triad normal.
- Artery.
- Vein; vein should be larger than the artery.
- Bile duct - round, has a lumen - approximately the size of the artery.
- Cuboidal epithelium, central nucleus, lightly basophilic cytoplasm.
- IHC: CK7 +ve.
- Irregular bile ducts without a lumen are called bile ductules; ductule implies a pathologic process.
- Lobule - hepatocytes.
- What zone has the defect?
- Cholestasis - absent/present.
- Presence of fibrosis?
- If a core biopsy is fragmented (on gross), think cirrhosis,[3] as cirrhotic livers commonly cleave at the fibrous bands.
- Grade the fibrosis.
- Central vein - has a collagen collar (seen on trichrome).
Pattern approach
| Common liver injury patterns | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hepatitis | Biliary | Steatosis | |||||||||||||||||||||
Hallmarks:
- Hepatitis - portal inflammation, lobular inflammation, interface hepatitis (inflammation at the portal-lobule interface).
- Clinical correlate: AST and ALT increased.
- Biliary - inflammation confined to the portal tract, cholestasis.
- Clinical correlate: ALP and GGT increased.
- Steatosis - fat.
- Clinical correlate: obese patient, changes on medical imaging (increased radiolucency on CT).
| Uncommon liver injury patterns | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Infiltrative | Congestive | Ischemic | Mass | Toxic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Hallmarks:
- Infiltrative - amyloid, monoclonal appearing lymphocytes.
- Clinical correlate: non-specific.
- Congestive - dilation of portal venules, perisinusoidal fibrosis/zone III fibrosis.
- Clinical correlates: heart failure, imaging finding (portal vein thrombosis), medications.
- Ischemic - necrosis.
- Clinical correlate - shock, known atherosclerosis, known cirrhosis.
- Mass - cellular atypia or architectural abnormality.
- Clinical correlate: mass on imaging.
- Toxic - almost anything.
- Clinical correlate: toxin ingestion.
Stains
- The stains ordered (initially) are dependent on the clinical history.
- Anything with "tumour", "mass", or "query metastasis" in the clinical history is "tumour".
- Stains:
- 3 H&E.
- Stains:
- Everything else is assumed to be "medical".
- Stains:
- PAS-D - to detect mucin.
- PAS - marks glycogen and mucin; useful for microvesicular steatosis
- Trichrome - to detect fibrosis/cirrhosis.
- Mallory trichrome: red = hepatocytes, blue/black = nuclei, green = fibrosis.
- Reticulin - demonstrates architecture.
- Iron stain.
- Grading (0-4): 0 = none, 1: only at high power, 2: at medium power, 3: at lowest power, 4: seen without microscope.
- One should comment on location, i.e. macrophage (Kupffer cell) vs. periportal hepatocytes vs. centrilobular hepatocytes vs. bile ducts vs. endothelial cells.
- Grading (0-4): 0 = none, 1: only at high power, 2: at medium power, 3: at lowest power, 4: seen without microscope.
- Stains:
- Anything with "tumour", "mass", or "query metastasis" in the clinical history is "tumour".
Additional stains/IHC
Non-standard stains:
Common IHC:[4]
- CK7 - bile ducts, and bile ductules +ve.
- CD34 - should be -ve in normal liver.
- CD34 marks endothelial cells - these are not present in a healthy liver lobule.
Liver biopsy
Medical liver biopsy adequacy
- This is covered in the medical liver disease article.
Reporting
- This is covered in the medical liver disease article.
Liver injury terms/histologic findings
Bile duct injury
- Non-specific finding.
- Seen in a number of conditions, e.g. autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis, viral hepatitis.
Microscopic:
- Abnormal epithelium:
- Nuclei not round.
- Cytoplasmic eosinophilia.
- Intraepithelial lymphocytes.
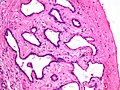
Bile duct hamartoma
- AKA Meyenburg complex and von Meyenburg complex.
- Classically associated with polycystic kidney disease (see medical liver disease).
- May be seen in a normal liver - incidental finding at autopsy in 0.5-5.6% of cases.[5]
- Appearance on ultrasound[6] and CT (hypodense)[7] - similar to metastases.
Microscopic:[8]
- Many bile ducts (tubular structures with cuboidal epithelium).
- Surrounded by a fibrous stroma.
Note:
- Not related to bile duct adenoma.
Images
www:
Isolated hepatic artery
- The hepatic artery branches within the liver should always be found together with a vein and bile duct.
DDx:
Ballooning degeneration
Ground glass hepatocytes
Mallory bodies
- Cytoplasmic inclusion.
- Represents: aggregation of denatured keratin filaments.
Appearance:
- "Twisted rope" appearance.[9]
- Eosinophilic.
- Green on trichrome.
- Associations:
- Often have PMNs around 'em.
- Often seen in hepatocytes undergoing ballooning degeneration.
Notes:
- Previously thought to indicate alcoholic liver disease; they are more common in alcohol.
Prevalence in common liver diseases (based on one study):[10]
| Disease | Prevalence |
|---|---|
| Alcoholic hepatitis | 65 % |
| Alcoholic cirrhosis | 51 % |
| Wilson's disease | 25 % |
| Primary biliary cirrhosis | 24 % |
| Nonalcoholic cirrhosis | 24 % |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | 23 % |
| Morbid obesity | 8 % |
Images
www:
Acidophilic body
- Seen in ASH and NASH.[11]
Appearance:
- Small (degenerative) hepatocyte with a:
- Pyknotic nucleus.
- Small, shrunken, pale staining.
- Eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- Pyknotic nucleus.
Notes:
- AKA Councilman-like bodies; see notes in Councilman bodies below.
Image
Councilman bodies
Appearance:
- Eosinophilic globule.
- Usu. surrounded by lymphocytes.
DDx:[12]
- Viral hepatitis.
- Yellow fever.
- Others.
Notes:
Inflammation
- Location and composition must be described, e.g. zone 1, lymphocytic infiltrate.
Grading
- Inflammation is usually often scored (0-4; 0 = nil, 1 = mild, 2 = moderate, 3 = moderate/marked, 4 = marked).
- The grade (usually) approximately corresponds to the transaminases.
Notes:
- Ishak[16] grades inflammation based on activity in the:
- Interface (0-4).
- Confluent (zone III) necrosis (0-6).
- Lobular necro-inflammation (0-4).
- Portal inflammation. (0-4).
Interface hepatitis
- May be referred to as piecemeal necrosis.[17]
- Non-specific finding, i.e. seen in several conditions - e.g. viral hepatitis, autoimmune hepatitis.
Features:
- Inflammation disrupts the "limiting plate", i.e. there is disruption of the hepatocytes that separate the portal tracts from the lobules.
Images
www:
Liver fibrosis
- More collagen than there should be.
- Assessment of fibrosis is based on the trichrome stain.
- Reticulin may be somewhat helpful.
- The normal reticulin pattern is chicken wire-like; in early pre-cirrhosis (Grade 1-2) the chicken wire is collapsed/flattened.
- Reticulin may be somewhat helpful.
The Toronto General Hospital uses the Laennec fibrosis system; named after the French chest physician.[19] This can be considered a modification of the Batts-Ludwig system,[20] which does not split Stage 4 into 4A, 4B and 4C.
Laennec fibrosis (stage):[21]
- Stage 0 - no fibrosis; "loose" strands of collagen - spaces between collagen bundles.
- Stage 1 - minimal fibrosis - no fibrous septa, minimal "portal expansion".
- Stage 2 - mild fibrosis; portal expansion, +/-delicate septa, +/-sinusoidal fibrosis.
- Stage 3 - moderate fibrosis - several fibrous septa, not bridging.
- Stage 4A - mild cirrhosis/definite or probable cirrhosis - delicate septa only, fragmentation with rounded fibrous septa.
- Stage 4B - moderate cirrhosis - at least some broad septa.
- Stage 4C - severe cirrhosis - large regions of "extinction", i.e. loss of normal parenchyma.
A simplified version:[22]
- Stage 0 - nil; loose strands of collagen.
- Stage 1 - portal expansion (minimal), no septa.
- Stage 2 - portal expansion (mild), few thin septa.
- Stage 3 - incomplete nodules.
- Stage 4 - complete nodules.
Notes:
- Many different staging schemes exist. Laennec is closely related to the Metavir scheme - which also assigns a score of 0-IV.
- There is a review by Theise focused on viral hepatitis.[18]
- Ishak[16] developed a 6-stage system (for research purposes).
Cirrhosis
Steatosis
Cholestasis
Diseases
The liver is an organ of many medical diseases.
Liver lesions
Includes pre-malignant lesions, i.e. dysplastic lesions, and malignant lesions, e.g. hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Liver mass DDx (simple)
Basic DDx of a liver mass (5 Hs):[23]
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
- Hydatid cyst.
- Liver hemangioma.
- Hepatic adenoma.
- Hyperplasia, focal nodular.
Cystic liver lesions
Radiologic DDx:[24]
- Bile duct cyst.
- Autosomal dominant polycystic liver disease.
- Biliary hamartoma.
- Caroli disease.
- Undifferentiated embryonal sarcoma.
- Biliary cystadenoma.
- Cystadenocarcinoma.
- Cystic metastasis.
- Pyogenic and amebic abscesses.
- Intrahepatic hydatid cyst.
- Extrapancreatic pseudocyst.
- Biloma.
- Intrahepatic hematoma.
See also
References
- ↑ Fine DR, Glasser D, Hildebrandt D, Esser J, Lurie RE, Chetty N (September 1995). "An anatomic and physiological model of hepatic vascular system". J. Appl. Physiol. 79 (3): 1008–26. PMID 8567497.
- ↑ Koo A, Liang IY, Cheng KK (October 1975). "The terminal hepatic microcirculation in the rat". Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci 60 (4): 261–6. PMID 1041797.
- ↑ Fung, S. October 2007.
- ↑ Pollet, A. 27 May 2009.
- ↑ Hepatic von Meyenburg complex: a trigger of severe portal hypertension. Yoshida S, Kurokohchi K, Ueno T, Yoshino M, Shimada M, Masaki T. Liver Int. 2009 Apr;29(4):614-5. Epub 2008 Oct 14. PMID 19018981. URL: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=2711260. Accessed on: 28 September 2009.
- ↑ Bile duct hamartomas--the von Meyenburg complex. Salles VJ, Marotta A, Netto JM, Speranzini MB, Martins MR. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2007 Feb;6(1):108-9. PMID 17287178.
- ↑ [The von Meyenburg complex] Schwab SA, Bautz W, Uder M, Kuefner MA. Rontgenpraxis. 2008;56(6):241-4. German. PMID 19294869.
- ↑ Burt, Alastair D.;Portmann, Bernard C.;Ferrell, Linda D. (2006). MacSween's Pathology of the Liver (5th ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 176. ISBN 978-0-443-10012-3.
- ↑ OA. September 9, 2009.
- ↑ Jensen K, Gluud C. The Mallory body: morphological, clinical and experimental studies (Part 1 of a literature survey). Hepatology. 1994 Oct;20(4 Pt 1):1061-77. Review. PMID 7927209.
- ↑ Tiniakos DG (2009). "Liver biopsy in alcoholic and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis patients". Gastroenterol. Clin. Biol. 33 (10-11): 930–9. doi:10.1016/j.gcb.2009.05.009. PMID 19646834.
- ↑ URL: http://www.tissueculturemicroscopy.com/degenerations-and-certain-infiltrations.html. Accessed on: 1 February 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/cytosegresome+formations. Accessed on: 1 February 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://www.tissueculturemicroscopy.com/degenerations-and-certain-infiltrations.html. Accessed on: 1 February 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://books.google.com/books?id=MrLfdTZl1dEC&pg=PA62#v=onepage&q&f=false. Accessed on: 1 February 2011.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Ishak K, Baptista A, Bianchi L, et al. (June 1995). "Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis". J. Hepatol. 22 (6): 696-9. PMID 7560864.
- ↑ Atlas of Pathology. URL: http://www.pathologyatlas.ro/viral-chronic-moderate-hepatitis.php. Accessed on: September 1, 2009.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Theise ND (February 2007). "Liver biopsy assessment in chronic viral hepatitis: a personal, practical approach". Mod. Pathol. 20 Suppl 1: S3-14. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800693. PMID 17486049. http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v20/n1s/full/3800693a.html.
- ↑ Why does cirrhosis belong to Laennec? Duffin JM. CMAJ. 1987 Sep 1;137(5):393-6. PMID 3304599. URL: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/pagerender.fcgi?artid=1492806&pageindex=4
- ↑ Batts KP, Ludwig J (December 1995). "Chronic hepatitis. An update on terminology and reporting". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 19 (12): 1409–17. PMID 7503362.
- ↑ URL: http://www.pulsus.com/cddw2000/abs/080.htm. Accessed on: 9 December 2010.
- ↑ OA. 10 September 2009.
- ↑ Greenwald, J.; Heng, M. (2007). Toronto Notes for Medical Students 2007 (2007 ed.). The Toronto Notes Inc. for Medical Students Inc.. pp. DM16. ISBN 978-0968592878.
- ↑ Mortelé, KJ.; Ros, PR.. "Cystic focal liver lesions in the adult: differential CT and MR imaging features.". Radiographics 21 (4): 895-910. PMID 11452064. http://radiographics.rsnajnls.org/cgi/content/abstract/21/4/895.