Difference between revisions of "Vascular disease"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (→Cholesterol embolism: w) |
(→Medial calcific sclerosis: split out) |
||
| (55 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The article covers '''vascular disease''', i.e. diseases of blood | The article covers '''vascular disease''', i.e. diseases of [[blood vessel]]s. These keep vascular surgeons and cardiac surgeon busy. | ||
Vasculitides are covered in a separate article called ''[[vasculitides]]''. | |||
==Normal blood vessels== | ==Normal blood vessels== | ||
Comparing arteries and veins:<ref>URL: [http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/vascular/vascular.htm http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/vascular/vascular.htm]. Accessed on: 13 January 2011.</ref> | Comparing arteries and veins:<ref>URL: [http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/vascular/vascular.htm http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/vascular/vascular.htm]. Accessed on: 13 January 2011.</ref> | ||
{| class="wikitable" | <center> | ||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | |||
! Feature | |||
! Artery | |||
! Vein | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Internal elastic lamina | | Internal elastic lamina (IEL) | ||
| prominent/thick, usu. complete | | prominent/thick, usu. complete | ||
| thin & incomplete | | thin & incomplete | ||
|- | |- | ||
| External elastic lamina | | External elastic lamina (EEL) | ||
| present, thick | | present, thick | ||
| absent | | absent | ||
| Line 24: | Line 27: | ||
| thin | | thin | ||
|} | |} | ||
</center> | |||
[[Image:2102 Comparison of Artery and Vein.jpg|thumb|400px|center|Artery and vein. (WC)]] | |||
==Great vessels== | ==Great vessels== | ||
| Line 30: | Line 35: | ||
==Atherosclerosis== | ==Atherosclerosis== | ||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
*[[Coronary artery atherosclerosis]] -> [[myocardial infarction]] +/-coronary thrombosis. | *A leading cause of death, esp. in the Western world. | ||
* | *May have multi-system manifestations. | ||
*Carotid artery atherosclerosis -> thrombotic stroke. | |||
Location and associated pathology: | |||
*[[Coronary artery atherosclerosis]] ([[AKA]] ''[[coronary artery disease]]'') -> [[myocardial infarction]] +/-coronary thrombosis. | |||
*[[Atherosclerotic peripheral vascular disease]] -> [[leg amputation]]s. | |||
*Carotid artery atherosclerosis -> thrombotic [[stroke]]. | |||
*Superior mesenteric artery atherosclerosis -> [[ischemic enteritis]] or [[ischemic colitis]] or ischemic enterocolitis. | |||
*Penile artery atherosclerosis -> impotence. | |||
Clinical risk factors: | Clinical risk factors: | ||
*Age. | *Age. | ||
*Blood pressure - modifiable (antihypertensives). | *[[Hypertension|Blood pressure (high)]] - modifiable (antihypertensives). | ||
*Cholesterol - modifiable (statins, diet). | *Cholesterol - modifiable (statins, diet). | ||
*[[Diabetes mellitus]] - modifiable (hypoglycemic medications, diet, lifestyle). | *[[Diabetes mellitus]] - modifiable (hypoglycemic medications, diet, lifestyle). | ||
| Line 50: | Line 61: | ||
*Luminal narrowing. | *Luminal narrowing. | ||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
| Line 58: | Line 67: | ||
**Thrombosis. | **Thrombosis. | ||
**Haemorrhage. | **Haemorrhage. | ||
====Image==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:RCA_atherosclerosis.jpg |Right coronary artery with atherosclerosis. (WC/Nephron) | |||
</gallery> | |||
===Stains=== | |||
*[[Elastic trichrome stain]] or [[Movat stain]] - highlights duplication of internal elastic lamina, allows on to identify with ease intimal thickening. | |||
==Aortic dissection== | ==Aortic dissection== | ||
*Abbreviated ''AoD''. | |||
{{Main|Aortic dissection}} | |||
*'' | |||
==Cystic medial degeneration== | ==Cystic medial degeneration== | ||
*[[AKA]] ''cystic medial necrosis''.<ref>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/756835-overview http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/756835-overview]. Accessed on: 12 August 2010.</ref> | *[[AKA]] ''cystic medial necrosis''.<ref>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/756835-overview http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/756835-overview]. Accessed on: 12 August 2010.</ref> | ||
{{Main|Cystic medial degeneration}} | |||
==Medial calcific sclerosis== | ==Medial calcific sclerosis== | ||
[[AKA]] ''Moenckeberg medial calcific sclerosis'', ''calcific medial sclerosis of Monckeberg'', and ''Monckeberg's arteriosclerosis''. | |||
{{Main|Medial calcific sclerosis}} | |||
==Hyperplastic arteriolosclerosis== | ==Hyperplastic arteriolosclerosis== | ||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
*Associated with:<ref>URL: [http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/IMMHTML/IMM028.html http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/IMMHTML/IMM028.html]. Accessed on: 11 May 2011.</ref> | *Associated with:<ref>URL: [http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/IMMHTML/IMM028.html http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/IMMHTML/IMM028.html]. Accessed on: 11 May 2011.</ref> | ||
**''Malignant [[hypertension]]''. | **''Malignant [[hypertension]]''. | ||
**''[[Scleroderma]]''. | **''[[Scleroderma]]''. | ||
*May be a consequence of [[thrombotic microangiopathy]].{{fact}} | |||
Note: | |||
*Hyperplasia = proliferation of cells. | |||
===Microscopic=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
| Line 164: | Line 132: | ||
Images: | Images: | ||
*[http://www.brown.edu/Courses/Digital_Path/systemic_path/cardio/fibromuscular-dysplasia.html FMD (brown.edu)]. | *[http://www.brown.edu/Courses/Digital_Path/systemic_path/cardio/fibromuscular-dysplasia.html FMD (brown.edu)]. | ||
*[http:// | *[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2721953/figure/F3/ FMD of AV nodal artery (kams.or.kr)].<ref name=pmid17179675/> | ||
===Stains=== | ===Stains=== | ||
*[[Elastic trichrome]] or [[Movat stain]] - to demonstrate elastic fibre fragmentation. | *[[Elastic trichrome]] or [[Movat stain]] - to demonstrate elastic fibre fragmentation. | ||
==Thromboangiitis obliterans== | ==Thromboangiitis obliterans== | ||
{{Main|Thromboangiitis obliterans}} | |||
==Thrombosis== | ==Thrombosis== | ||
| Line 209: | Line 162: | ||
*Fibrin - pink acellular stuff on a [[H&E stain]]. | *Fibrin - pink acellular stuff on a [[H&E stain]]. | ||
Image | ====Image==== | ||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Fetal_thrombotic_vasculopathy_-_high_mag.jpg | Intravascular fibrin - high mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Cholesterol embolism== | |||
*Abbreviated ''CE''. | |||
{{Main|Cholesterol embolism}} | |||
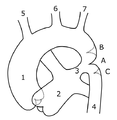
== | ==Coarctation of the aorta== | ||
*[[AKA]] ''aortic coarctation''. | |||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
* | *Uncommon. | ||
Classification: | |||
*Preductal. | |||
* | *Postductal. | ||
Associations: | |||
*[[Bicuspid aortic valve]].<ref name=pmid16129122>{{Cite journal | last1 = Braverman | first1 = AC. | last2 = Güven | first2 = H. | last3 = Beardslee | first3 = MA. | last4 = Makan | first4 = M. | last5 = Kates | first5 = AM. | last6 = Moon | first6 = MR. | title = The bicuspid aortic valve. | journal = Curr Probl Cardiol | volume = 30 | issue = 9 | pages = 470-522 | month = Sep | year = 2005 | doi = 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2005.06.002 | PMID = 16129122 }}</ref> | |||
*[[Turner syndrome]].<ref name=pmid20222980>{{Cite journal | last1 = Hjerrild | first1 = BE. | last2 = Mortensen | first2 = KH. | last3 = Sørensen | first3 = KE. | last4 = Pedersen | first4 = EM. | last5 = Andersen | first5 = NH. | last6 = Lundorf | first6 = E. | last7 = Hansen | first7 = KW. | last8 = Hørlyck | first8 = A. | last9 = Hager | first9 = A. | title = Thoracic aortopathy in Turner syndrome and the influence of bicuspid aortic valves and blood pressure: a CMR study. | journal = J Cardiovasc Magn Reson | volume = 12 | issue = | pages = 12 | month = | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1186/1532-429X-12-12 | PMID = 20222980 }}</ref> | |||
====Clinical==== | |||
* | Presentation:<ref name=pmid20391897>{{Cite journal | last1 = Peres | first1 = A. | last2 = Martins | first2 = JD. | last3 = Paramés | first3 = F. | last4 = Gil | first4 = R. | last5 = Matias | first5 = C. | last6 = Franco | first6 = J. | last7 = Freitas | first7 = I. | last8 = Trigo | first8 = C. | last9 = Fragata | first9 = J. | title = Isolated aortic coarctation: experience in 100 consecutive patients. | journal = Rev Port Cardiol | volume = 29 | issue = 1 | pages = 23-35 | month = Jan | year = 2010 | doi = | PMID = 20391897 }}</ref> | ||
*Heart failure. | |||
*[[Hypertension]] - esp. upper extremity vs. lower extremity. | |||
===Gross=== | |||
* | *Narrowing (stenosis) of the aorta proximal or distal to the ductus arteriosis. | ||
====Image==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Coarctation_and_PDA.png | Pre- and postductal coarctation of the aorta - schematic (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Intracranial berry aneurysm== | |||
{{Main|Berry aneurysm}} | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 03:39, 7 March 2016
The article covers vascular disease, i.e. diseases of blood vessels. These keep vascular surgeons and cardiac surgeon busy.
Vasculitides are covered in a separate article called vasculitides.
Normal blood vessels
Comparing arteries and veins:[1]
| Feature | Artery | Vein |
|---|---|---|
| Internal elastic lamina (IEL) | prominent/thick, usu. complete | thin & incomplete |
| External elastic lamina (EEL) | present, thick | absent |
| Shape | circular / lumen wide open | collapsed |
| Wall thickness | thick | thin |
Great vessels
When things go wrong here, you see a cardiac surgeon.
Atherosclerosis
General
- A leading cause of death, esp. in the Western world.
- May have multi-system manifestations.
Location and associated pathology:
- Coronary artery atherosclerosis (AKA coronary artery disease) -> myocardial infarction +/-coronary thrombosis.
- Atherosclerotic peripheral vascular disease -> leg amputations.
- Carotid artery atherosclerosis -> thrombotic stroke.
- Superior mesenteric artery atherosclerosis -> ischemic enteritis or ischemic colitis or ischemic enterocolitis.
- Penile artery atherosclerosis -> impotence.
Clinical risk factors:
- Age.
- Blood pressure (high) - modifiable (antihypertensives).
- Cholesterol - modifiable (statins, diet).
- Diabetes mellitus - modifiable (hypoglycemic medications, diet, lifestyle).
- Smoking - modifiable (cessation).
- Family history.
Microscopic
Features:
- Intimal hyperplasia.
- Lipid deposition.
- Foamy macrophages within intima & media.
- Cholesterol clefts
- Luminal narrowing.
Notes:
- Considered "complex" if any of the following are present:[2]
- Calcifications.
- Thrombosis.
- Haemorrhage.
Image
Stains
- Elastic trichrome stain or Movat stain - highlights duplication of internal elastic lamina, allows on to identify with ease intimal thickening.
Aortic dissection
- Abbreviated AoD.
Main article: Aortic dissection
Cystic medial degeneration
Main article: Cystic medial degeneration
Medial calcific sclerosis
AKA Moenckeberg medial calcific sclerosis, calcific medial sclerosis of Monckeberg, and Monckeberg's arteriosclerosis.
Main article: Medial calcific sclerosis
Hyperplastic arteriolosclerosis
General
- Associated with:[4]
- Malignant hypertension.
- Scleroderma.
- May be a consequence of thrombotic microangiopathy.[citation needed]
Note:
- Hyperplasia = proliferation of cells.
Microscopic
Features:[5]
- Onion-skin appearance of intima & media due to:
- Intimal hyperplasia.
- Smooth muscle hyperplasia.
Image: Hyperplastic arteriolosclerosis (utah.edu).
Fibromuscular dysplasia
- Abbreviated FMD.
General
Etiology:
- Unknown, possibly genetic.
Gender:
- Women > men.
- May be seen in virtually any artery.
- Reported as a cause of sudden death with involvement of the artery supplying the AV node.[6]
Gross/radiologic
- Segmental - thinning and thickening.[7]
Classical locations:[7]
- Renal artery - leading to hypertension.
- Carotid artery.
Microscopic
Features:[7]
- Smooth muscle hyperplasia - key feature.
- Elastic fibre fragmentation.
- Luminal narrowing.
Images:
Stains
- Elastic trichrome or Movat stain - to demonstrate elastic fibre fragmentation.
Thromboangiitis obliterans
Main article: Thromboangiitis obliterans
Thrombosis
- See also: Cerebral venous thrombosis.
General
Definition:
- Blood clot formation within a vessel.
Complications:
- Embolism - see: Pulmonary thromboembolism.
Risk factors:
- The classic pimping question is what "Virchow's triad?"
- Stasis, hypercoagulability, endothelial injury.
- A long list is found in: risk factors for VTE.
Gross
Microscopic
Features:
- Lines of Zahn.
- Fibrin - pink acellular stuff on a H&E stain.
Image
Cholesterol embolism
- Abbreviated CE.
Main article: Cholesterol embolism
Coarctation of the aorta
- AKA aortic coarctation.
General
- Uncommon.
Classification:
- Preductal.
- Postductal.
Associations:
Clinical
Presentation:[10]
- Heart failure.
- Hypertension - esp. upper extremity vs. lower extremity.
Gross
- Narrowing (stenosis) of the aorta proximal or distal to the ductus arteriosis.
Image
Intracranial berry aneurysm
Main article: Berry aneurysm
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/vascular/vascular.htm. Accessed on: 13 January 2011.
- ↑ Klatt, Edward C. (2006). Robbins and Cotran Atlas of Pathology (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 4. ISBN 978-1416002741.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/756835-overview. Accessed on: 12 August 2010.
- ↑ URL: http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/IMMHTML/IMM028.html. Accessed on: 11 May 2011.
- ↑ Klatt, Edward C. (2006). Robbins and Cotran Atlas of Pathology (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 7. ISBN 978-1416002741.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Lee, S.; Chae, J.; Cho, Y. (Dec 2006). "Causes of sudden death related to sexual activity: results of a medicolegal postmortem study from 2001 to 2005.". J Korean Med Sci 21 (6): 995-9. PMID 17179675.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Hata, D. (Sep 2001). "Fibromuscular dysplasia.". Intern Med 40 (9): 978-9. PMID 11579971.
- ↑ Braverman, AC.; Güven, H.; Beardslee, MA.; Makan, M.; Kates, AM.; Moon, MR. (Sep 2005). "The bicuspid aortic valve.". Curr Probl Cardiol 30 (9): 470-522. doi:10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2005.06.002. PMID 16129122.
- ↑ Hjerrild, BE.; Mortensen, KH.; Sørensen, KE.; Pedersen, EM.; Andersen, NH.; Lundorf, E.; Hansen, KW.; Hørlyck, A. et al. (2010). "Thoracic aortopathy in Turner syndrome and the influence of bicuspid aortic valves and blood pressure: a CMR study.". J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 12: 12. doi:10.1186/1532-429X-12-12. PMID 20222980.
- ↑ Peres, A.; Martins, JD.; Paramés, F.; Gil, R.; Matias, C.; Franco, J.; Freitas, I.; Trigo, C. et al. (Jan 2010). "Isolated aortic coarctation: experience in 100 consecutive patients.". Rev Port Cardiol 29 (1): 23-35. PMID 20391897.