Difference between revisions of "Histiocytoses"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→IHC: redo ref.) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Histiocytoses''', singular '''histiocytosis''', are a rare set of conditions affecting tissue macrophages. | '''Histiocytoses''', singular '''histiocytosis''', are a rare set of conditions affecting tissue macrophages. | ||
== | ==Historical classification of histiocytoses in a table== | ||
Features of histiocytoses:<ref>{{Ref Sternberg4|479}}</ref> | Features of histiocytoses:<ref>{{Ref Sternberg4|479}}</ref> | ||
{| class="wikitable" border="1" | {| class="wikitable" border="1" | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
! | ! | ||
! Histologic features | ! Histologic features | ||
! [[EM]] features | ! [[Electron microscopy|EM]] features | ||
! CD68 | ! CD68 | ||
! S-100 | ! S-100 | ||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
*''EM'' = [[electron microscopy]]. | *''EM'' = [[electron microscopy]]. | ||
The classification has evolved considerably, as the entities can overlap. An overview of a more recent classification is found in the article ''[[classification of histiocytoses and neoplasms of the macrophage-dendritic cell lineages]]''. | |||
==Langerhans cell histiocytosis== | ==Langerhans cell histiocytosis== | ||
| Line 57: | Line 59: | ||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
*Rare. | *Rare. | ||
* | *Clonal proliferation of histiocytes; 3 of 5 cases shown monoclonal by Chetritt ''el al''.<ref name=pmid10492045>{{Cite journal | last1 = Chetritt | first1 = J. | last2 = Paradis | first2 = V. | last3 = Dargere | first3 = D. | last4 = Adle-Biassette | first4 = H. | last5 = Maurage | first5 = CA. | last6 = Mussini | first6 = JM. | last7 = Vital | first7 = A. | last8 = Wechsler | first8 = J. | last9 = Bedossa | first9 = P. | title = Chester-Erdheim disease: a neoplastic disorder. | journal = Hum Pathol | volume = 30 | issue = 9 | pages = 1093-6 | month = Sep | year = 1999 | doi = 10.1016/s0046-8177(99)90228-9 | PMID = 10492045 }}</ref> | ||
===Gross=== | ===Gross=== | ||
| Line 63: | Line 65: | ||
*Bone involvement - classic. | *Bone involvement - classic. | ||
*Usually multiple systems are involved. | *Usually multiple systems are involved. | ||
Note: | |||
*Does ''not'' usually involve the lymph nodes - like [[Rosai-Dorfman disease]]. | |||
===Microscopic=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
| Line 75: | Line 80: | ||
*[[Langerhans cell histiocytosis]]. | *[[Langerhans cell histiocytosis]]. | ||
Images: | ====Images==== | ||
<gallery> | |||
Image: Maladie de Chester-Erdheim.png |EHC. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1770491/figure/f1/ ECD (nih.gov)]. | *[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1770491/figure/f1/ ECD (nih.gov)]. | ||
| Line 89: | Line 98: | ||
*[[Neuropathology]]. | *[[Neuropathology]]. | ||
*[[Hemophagocytic syndrome]]. | *[[Hemophagocytic syndrome]]. | ||
*[[Histiocytic sarcoma]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 18:55, 23 July 2019
Histiocytoses, singular histiocytosis, are a rare set of conditions affecting tissue macrophages.
Historical classification of histiocytoses in a table
Features of histiocytoses:[1]
| Histologic features | EM features | CD68 | S-100 | CD1a | Image | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Macrophage | epithelioid cells, giant cells | - | + | - | - | Macrophages - CD68 (WC) |
| Erdheim-Chester disease | Touton giant cells | - | + | +/- | - | ECD (upmc.edu) |
| Rosai-Dorfman | Emperipolesis | - | + | + | - | RDD (WC) |
| Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) | Reniform nuclei, eosinophilic cytoplasm |
Birbeck granules | + | + | + | LCH (WC) |
Notes:
- EM = electron microscopy.
The classification has evolved considerably, as the entities can overlap. An overview of a more recent classification is found in the article classification of histiocytoses and neoplasms of the macrophage-dendritic cell lineages.
Langerhans cell histiocytosis
Main article: Langerhans cell histiocytosis
IHC
Langerin (CD207).[2]
Erdheim-Chester disease
- Abbreviated ECD.
General
- Rare.
- Clonal proliferation of histiocytes; 3 of 5 cases shown monoclonal by Chetritt el al.[3]
Gross
Features:
- Bone involvement - classic.
- Usually multiple systems are involved.
Note:
- Does not usually involve the lymph nodes - like Rosai-Dorfman disease.
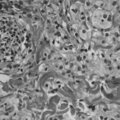
Microscopic
Features:[4]
- Foamy histocytes.
- Large cells with gray, bubbly cytoplasm.
- +/-Touton giant cells - very distinctive histiocytes - classic.
- Nuclei form a ring around the cell periphery.
DDx:
Images
www:
IHC
Features:[5]
- CD68 +ve.
- S100 -ve/+ve.
- CD1a -ve.
See also
References
- ↑ Mills, Stacey E; Carter, Darryl; Greenson, Joel K; Oberman, Harold A; Reuter, Victor E (2004). Sternberg's Diagnostic Surgical Pathology (4th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 479. ISBN 978-0781740517.
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 604862
- ↑ Chetritt, J.; Paradis, V.; Dargere, D.; Adle-Biassette, H.; Maurage, CA.; Mussini, JM.; Vital, A.; Wechsler, J. et al. (Sep 1999). "Chester-Erdheim disease: a neoplastic disorder.". Hum Pathol 30 (9): 1093-6. doi:10.1016/s0046-8177(99)90228-9. PMID 10492045.
- ↑ Sheu, SY.; Wenzel, RR.; Kersting, C.; Merten, R.; Otterbach, F.; Schmid, KW. (Nov 2004). "Erdheim-Chester disease: case report with multisystemic manifestations including testes, thyroid, and lymph nodes, and a review of literature.". J Clin Pathol 57 (11): 1225-8. doi:10.1136/jcp.2004.018481. PMID 15509691.
- ↑ Haroche, J.; Amoura, Z.; Touraine, P.; Seilhean, D.; Graef, C.; Birmelé, B.; Wechsler, B.; Cluzel, P. et al. (Jun 2007). "Bilateral adrenal infiltration in Erdheim-Chester disease. Report of seven cases and literature review.". J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92 (6): 2007-12. doi:10.1210/jc.2006-2018. PMID 17405844.