Difference between revisions of "Hemangioblastoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(more) |
Jensflorian (talk | contribs) (update + pictures) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = Hemangioblastoma Histology HE.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
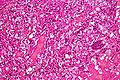
| Caption = Cerebellar hemangioblastoma. | |||
| Synonyms = | |||
| Micro = vascular tumour with large polygonal stromal cells with hyperchromatic nuclei and vacuolar cytoplasm | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = metastatic [[clear cell renal cell carcinoma]] | |||
| Stains = | |||
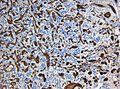
| IHC = alpha-inhibin +ve, NSE +ve, EMA -ve | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = brain - usu. [[cerebellum]] | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = [[von Hippel-Lindau disease]] | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = good (WHO grade I) | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
| Tx = | |||
}} | |||
'''Hemangioblastoma''' is a low grade [[brain tumour]] tumour typically found the [[cerebellum]]. | '''Hemangioblastoma''' is a low grade [[brain tumour]] tumour typically found the [[cerebellum]]. | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
*Usually ''cerebellar''. | *Usually ''cerebellar''. | ||
**occassionally brainstem or spinal cord. Supratentorial tumors are exceptionally rare. | |||
*Typically in adults.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Kassardjian | first1 = CD. | last2 = Macdonald | first2 = RL. | last3 = Munoz | first3 = DG. | title = Hemangioblastomas in the elderly: epidemiology and clinical characteristics. | journal = J Clin Neurosci | volume = 21 | issue = 7 | pages = 1205-8 | month = Jul | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1016/j.jocn.2013.10.023 | PMID = 24629394 }}</ref> | |||
*Associated with [[von Hippel-Lindau syndrome]]. | *Associated with [[von Hippel-Lindau syndrome]]. | ||
*WHO grade I.<ref>URL: [http://www.expertconsultbook.com/expertconsult/ob/book.do?method=display&type=bookPage&decorator=none&eid=4-u1.0-B978-1-4160-4580-9..00019-8--sc0155&isbn=978-1-4160-4580-9 http://www.expertconsultbook.com/expertconsult/ob/book.do?method=display&type=bookPage&decorator=none&eid=4-u1.0-B978-1-4160-4580-9..00019-8--sc0155&isbn=978-1-4160-4580-9]. Accessed on: 9 December 2010.</ref> | *Symptomatic when CSF flow is impaired. | ||
*WHO grade I (ICD-O: 9161/1).<ref>URL: [http://www.expertconsultbook.com/expertconsult/ob/book.do?method=display&type=bookPage&decorator=none&eid=4-u1.0-B978-1-4160-4580-9..00019-8--sc0155&isbn=978-1-4160-4580-9 http://www.expertconsultbook.com/expertconsult/ob/book.do?method=display&type=bookPage&decorator=none&eid=4-u1.0-B978-1-4160-4580-9..00019-8--sc0155&isbn=978-1-4160-4580-9]. Accessed on: 9 December 2010.</ref> | |||
==Macroscopy== | |||
*Red to yellow nodules, highly vascularized. | |||
*75% are cystic tumors. | |||
**Peripheral solid portion. | |||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
| Line 12: | Line 52: | ||
**Hyperchromatic nuclei. | **Hyperchromatic nuclei. | ||
**Vacuolar cytoplasm. | **Vacuolar cytoplasm. | ||
*Occassionally extensive sclerosis. | |||
Note: | |||
*Based on the stromal content, some classify the tumors as "cellular" and "reticular".<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Hasselblatt | first1 = M. | last2 = Jeibmann | first2 = A. | last3 = Gerss | first3 = J. | last4 = Behrens | first4 = C. | last5 = Rama | first5 = B. | last6 = Wassmann | first6 = H. | last7 = Paulus | first7 = W. | title = Cellular and reticular variants of haemangioblastoma revisited: a clinicopathologic study of 88 cases. | journal = Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol | volume = 31 | issue = 6 | pages = 618-22 | month = Dec | year = 2005 | doi = 10.1111/j.1365-2990.2005.00669.x | PMID = 16281910 }}</ref> | |||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
| Line 21: | Line 66: | ||
Image:Cerebellar_hemangioblastoma_high_mag.jpg | Hemangioblastoma - high mag. (WC) | Image:Cerebellar_hemangioblastoma_high_mag.jpg | Hemangioblastoma - high mag. (WC) | ||
Image:Hemangioblastoma_-_nse_-_intermed_mag.jpg | Hemangioblastoma - NSE - intermed. mag. (WC) | Image:Hemangioblastoma_-_nse_-_intermed_mag.jpg | Hemangioblastoma - NSE - intermed. mag. (WC) | ||
File:Hemangioblastoma - nse - high mag.jpg | Hemangioblastoma - NSE - high mag. (WC) | |||
File:Hemangioblastoma Histology CD31.jpg | Hemangioblastoma - CD31. (WC/marvin101) | |||
File:Hippel Lindau.gif | Hemangioblastomas in Hippel-Lindau disease (PlosONE). | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
www: | www: | ||
| Line 32: | Line 80: | ||
*NSE +ve (nucleus + cytoplasm). | *NSE +ve (nucleus + cytoplasm). | ||
**RCC typically -ve. | **RCC typically -ve. | ||
*CK -ve. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 07:48, 22 May 2015
| Hemangioblastoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
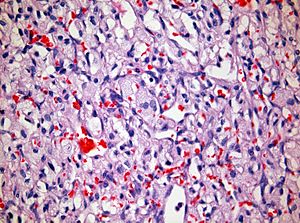 Cerebellar hemangioblastoma. | |
|
| |
| LM | vascular tumour with large polygonal stromal cells with hyperchromatic nuclei and vacuolar cytoplasm |
| LM DDx | metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma |
| IHC | alpha-inhibin +ve, NSE +ve, EMA -ve |
| Site | brain - usu. cerebellum |
|
| |
| Syndromes | von Hippel-Lindau disease |
|
| |
| Prognosis | good (WHO grade I) |
Hemangioblastoma is a low grade brain tumour tumour typically found the cerebellum.
General
- Usually cerebellar.
- occassionally brainstem or spinal cord. Supratentorial tumors are exceptionally rare.
- Typically in adults.[1]
- Associated with von Hippel-Lindau syndrome.
- Symptomatic when CSF flow is impaired.
- WHO grade I (ICD-O: 9161/1).[2]
Macroscopy
- Red to yellow nodules, highly vascularized.
- 75% are cystic tumors.
- Peripheral solid portion.
Microscopic
Features:[3]
- Vascular.
- Polygonal stromal cells with:
- Hyperchromatic nuclei.
- Vacuolar cytoplasm.
- Occassionally extensive sclerosis.
Note:
- Based on the stromal content, some classify the tumors as "cellular" and "reticular".[4]
DDx:
- Metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
Images
www:
IHC
Features:[5]
- Alpha-inhibin +ve (cytoplasm).
- EMA -ve.
- RCC typically +ve.
- NSE +ve (nucleus + cytoplasm).
- RCC typically -ve.
- CK -ve.
See also
References
- ↑ Kassardjian, CD.; Macdonald, RL.; Munoz, DG. (Jul 2014). "Hemangioblastomas in the elderly: epidemiology and clinical characteristics.". J Clin Neurosci 21 (7): 1205-8. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2013.10.023. PMID 24629394.
- ↑ URL: http://www.expertconsultbook.com/expertconsult/ob/book.do?method=display&type=bookPage&decorator=none&eid=4-u1.0-B978-1-4160-4580-9..00019-8--sc0155&isbn=978-1-4160-4580-9. Accessed on: 9 December 2010.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/340994-media. Accessed on: 23 June 2010.
- ↑ Hasselblatt, M.; Jeibmann, A.; Gerss, J.; Behrens, C.; Rama, B.; Wassmann, H.; Paulus, W. (Dec 2005). "Cellular and reticular variants of haemangioblastoma revisited: a clinicopathologic study of 88 cases.". Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 31 (6): 618-22. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2005.00669.x. PMID 16281910.
- ↑ URL: http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v18/n6/full/3800351a.html. Accessed on: 9 December 2010.