Difference between revisions of "Vermiform appendix"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Goblet cell carcinoid: +image) |
|||
| (100 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The ''' | The '''vermiform appendix''', usually just '''appendix''', is a little thingy that is attached to the [[cecum]]. Taking it out is the bread 'n butter of [[general surgery]]. | ||
The appendix is a vestigial structure that is thought to have arisen from a larger cecum. Larger cecae are often seen in herbivores and thought to facilitate better digestion of plant matter.<ref>{{cite book |author=Dawkins, R. |title=The Greatest Show on Earth: The Evidence for Evolution |publisher=Free Press |location= |year=2009 |pages=115 |edition=1st |isbn=978-1416594789 |oclc= |doi= |accessdate=}}</ref> | The appendix is a vestigial structure that is thought to have arisen from a larger cecum. Larger cecae are often seen in herbivores and thought to facilitate better digestion of plant matter.<ref>{{cite book |author=Dawkins, R. |title=The Greatest Show on Earth: The Evidence for Evolution |publisher=Free Press |location= |year=2009 |pages=115 |edition=1st |isbn=978-1416594789 |oclc= |doi= |accessdate=}}</ref> | ||
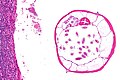
=Normal= | |||
== | ==Normal vermiform appendix== | ||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
* | *Seen in: | ||
* | **Right hemicolectomies. | ||
***[[colorectal carcinoma|Colon cancer]]. | |||
***[[Crohn's disease]]. | |||
**Surgeries for ovarian mucinous tumours. | |||
===Gross=== | ===Gross=== | ||
*Shiny serosal surface. | |||
* | **No exudate. | ||
* | *Normal diameter. | ||
*+/- | **6.6 +/- 1.5 mm -- based on CT.<ref name=pmid21344807>{{Cite journal | last1 = Charoensak | first1 = A. | last2 = Pongpornsup | first2 = S. | last3 = Suthikeeree | first3 = W. | title = Wall thickness and outer diameter of the normal appendix in adults using 64 slices multidetector CT. | journal = J Med Assoc Thai | volume = 93 | issue = 12 | pages = 1437-42 | month = Dec | year = 2010 | doi = | PMID = 21344807 }}</ref> | ||
=== | |||
===Microscopic=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
*+/-Lymphoid hyperplasia - mucosa or submucosa. | |||
* +/- | *Normal colorectal-type mucosa. | ||
* | *Fatty submucosa. | ||
*Benign smooth muscle. | |||
*Serosa. | |||
Negatives: | |||
* | *No [[neutrophil]]s in the muscularis propria. | ||
* | *No lesion in appendiceal tip. | ||
* | *No serosal inflammation ([[periappendicitis]]). | ||
* | *No organisms in the appendiceal lumen, e.g. [[Enterobius vermicularis]]. | ||
DDx: | |||
*[[Adenovirus appendicitis]]. | |||
* | *[[Cryptosporidiosis]]. | ||
*Mild colitis. | |||
===Sign out=== | |||
<pre> | |||
VERMIFORM APPENDIX WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS. | |||
</pre> | |||
Note: | |||
*This is for a normal appendix within a larger operation. The article ''[[negative appendectomy]]'' deals with a normal appearing appendix that was removed for presumed appendicitis. | |||
* | |||
== | ==Negative appendectomy== | ||
{{Main|Negative appendectomy}} | |||
An appendectomy done for presumed [[acute appendicitis]] that is pathologically within normal limits | |||
== | =Inflammatory pathologies= | ||
==Acute appendicitis== | |||
{{Main|Acute appendicitis}} | |||
==Adenovirus appendicitis== | |||
{{Main|Adenovirus appendicitis}} | |||
==Enterobius vermicularis== | |||
{| | {{Main|Enterobius vermicularis}} | ||
| | *[[AKA]] ''pinworm''. | ||
|- | ===General=== | ||
| | *May be found in the appendix. | ||
| | *The incidence is higher in normal appendices than inflamed ones.<ref name=pmid1853157>{{Cite journal | last1 = Wiebe | first1 = BM. | title = Appendicitis and Enterobius vermicularis. | journal = Scand J Gastroenterol | volume = 26 | issue = 3 | pages = 336-8 | month = Mar | year = 1991 | doi = | PMID = 1853157 }}</ref><ref name=pmid7945067/> | ||
| | *Clinically mimics appendicitis.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Ariyarathenam AV, Nachimuthu S, Tang TY, Courtney ED, Harris SA, Harris AM |title=Enterobius vermicularis infestation of the appendix and management at the time of laparoscopic appendectomy: case series and literature review |journal=Int J Surg |volume=8 |issue=6 |pages=466–9 |year=2010 |pmid=20637320 |doi=10.1016/j.ijsu.2010.06.007 |url=}}</ref> | ||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Features: | |||
* | *Usu. the appendiceal wall has no inflammation, i.e. there is no appendicitis.<ref name=pmid1853157/><ref name=pmid7945067>{{Cite journal | last1 = Dahlstrom | first1 = JE. | last2 = Macarthur | first2 = EB. | title = Enterobius vermicularis: a possible cause of symptoms resembling appendicitis. | journal = Aust N Z J Surg | volume = 64 | issue = 10 | pages = 692-4 | month = Oct | year = 1994 | doi = | PMID = 7945067 }}</ref> | ||
*''[[Enterobius vermicularis]]'' organisms. | |||
* | |||
====Image==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Enterobius_-_very_low_mag.jpg | Enterobius - very low mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Enterobius_-_high_mag.jpg | Enterobius - high mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Pinworms_in_the_Appendix_%281%29.jpg | Pinworm (WC/Uthman) | |||
</gallery> | |||
=== | ==Granulomatous appendicitis== | ||
{{Main|Granulomatous appendicitis}} | |||
=== | ==Inflammatory bowel disease== | ||
: See ''[[Inflammatory bowel disease]]''. | |||
== | ==Periappendicitis== | ||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
Definition: inflammation of tissues around the (vermiform) appendix.<ref>URL: [http://www.medilexicon.com/medicaldictionary.php?t=66889 http://www.medilexicon.com/medicaldictionary.php?t=66889]. Accessed on: 1 June 2011.</ref> | |||
*May be seen in association of appendicitis or alone. | |||
**With appendicitis it is suggestive of perforation. | |||
**Without concurrent appendicitis it is suggestive of another abdominal pathology.<ref name=pmid2349982>{{Cite journal | last1 = Fink | first1 = AS. | last2 = Kosakowski | first2 = CA. | last3 = Hiatt | first3 = JR. | last4 = Cochran | first4 = AJ. | title = Periappendicitis is a significant clinical finding. | journal = Am J Surg | volume = 159 | issue = 6 | pages = 564-8 | month = Jun | year = 1990 | doi = | PMID = 2349982 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = O'Neil | first1 = MB. | last2 = Moore | first2 = DB. | title = Periappendicitis: Clinical reality or pathologic curiosity? | journal = Am J Surg | volume = 134 | issue = 3 | pages = 356-7 | month = Sep | year = 1977 | doi = | PMID = 900337 }}</ref> | |||
===Microscopic=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
* | *Acute inflammation of the serosa. | ||
** | **[[Neutrophil]]s in the serosa. | ||
DDx: | |||
*[ | *[[Acute appendicitis]]. | ||
=== | =Tumours of the appendix= | ||
* | ==Adenocarcinoma== | ||
*Like ''colorectal adenocarcinoma'' - see ''[[colorectal tumours]]''. | |||
==Mucinous tumours of the appendix== | |||
{{Main|Mucinous tumours of the appendix}} | |||
This grouping includes ''mucinous cystadenoma'' and ''mucinous cystadenocarcinoma''. | |||
* | ==Goblet cell adenocarcinoma== | ||
{{Main|Goblet cell adenocarcinoma}} | |||
*Previously known as ''goblet cell carcinoid''. | |||
==Neuroendocrine tumour of the appendix== | |||
* | *Previously known as ''appendiceal carcinoid''. | ||
*[[AKA]] ''appendiceal neuroendocrine tumour'', abbreviated ''appendiceal NET''. | |||
{{Main|Neuroendocrine tumour of the appendix}} | |||
=See also= | |||
*[[Colon]]. | *[[Colon]]. | ||
*[[Gastrointestinal pathology]]. | *[[Gastrointestinal pathology]]. | ||
=References= | |||
{{reflist|2}} | {{reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category:Gastrointestinal pathology]] | [[Category:Gastrointestinal pathology]] | ||
[[Category:Vermiform appendix]] | |||
Latest revision as of 15:11, 4 December 2023
The vermiform appendix, usually just appendix, is a little thingy that is attached to the cecum. Taking it out is the bread 'n butter of general surgery.
The appendix is a vestigial structure that is thought to have arisen from a larger cecum. Larger cecae are often seen in herbivores and thought to facilitate better digestion of plant matter.[1]
Normal
Normal vermiform appendix
General
- Seen in:
- Right hemicolectomies.
- Surgeries for ovarian mucinous tumours.
Gross
- Shiny serosal surface.
- No exudate.
- Normal diameter.
- 6.6 +/- 1.5 mm -- based on CT.[2]
Microscopic
Features:
- +/-Lymphoid hyperplasia - mucosa or submucosa.
- Normal colorectal-type mucosa.
- Fatty submucosa.
- Benign smooth muscle.
- Serosa.
Negatives:
- No neutrophils in the muscularis propria.
- No lesion in appendiceal tip.
- No serosal inflammation (periappendicitis).
- No organisms in the appendiceal lumen, e.g. Enterobius vermicularis.
DDx:
- Adenovirus appendicitis.
- Cryptosporidiosis.
- Mild colitis.
Sign out
VERMIFORM APPENDIX WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS.
Note:
- This is for a normal appendix within a larger operation. The article negative appendectomy deals with a normal appearing appendix that was removed for presumed appendicitis.
Negative appendectomy
Main article: Negative appendectomy
An appendectomy done for presumed acute appendicitis that is pathologically within normal limits
Inflammatory pathologies
Acute appendicitis
Main article: Acute appendicitis
Adenovirus appendicitis
Main article: Adenovirus appendicitis
Enterobius vermicularis
Main article: Enterobius vermicularis
- AKA pinworm.
General
- May be found in the appendix.
- The incidence is higher in normal appendices than inflamed ones.[3][4]
- Clinically mimics appendicitis.[5]
Microscopic
Features:
- Usu. the appendiceal wall has no inflammation, i.e. there is no appendicitis.[3][4]
- Enterobius vermicularis organisms.
Image
Granulomatous appendicitis
Main article: Granulomatous appendicitis
Inflammatory bowel disease
Periappendicitis
General
Definition: inflammation of tissues around the (vermiform) appendix.[6]
- May be seen in association of appendicitis or alone.
Microscopic
Features:
- Acute inflammation of the serosa.
- Neutrophils in the serosa.
DDx:
Tumours of the appendix
Adenocarcinoma
- Like colorectal adenocarcinoma - see colorectal tumours.
Mucinous tumours of the appendix
Main article: Mucinous tumours of the appendix
This grouping includes mucinous cystadenoma and mucinous cystadenocarcinoma.
Goblet cell adenocarcinoma
Main article: Goblet cell adenocarcinoma
- Previously known as goblet cell carcinoid.
Neuroendocrine tumour of the appendix
- Previously known as appendiceal carcinoid.
- AKA appendiceal neuroendocrine tumour, abbreviated appendiceal NET.
Main article: Neuroendocrine tumour of the appendix
See also
References
- ↑ Dawkins, R. (2009). The Greatest Show on Earth: The Evidence for Evolution (1st ed.). Free Press. pp. 115. ISBN 978-1416594789.
- ↑ Charoensak, A.; Pongpornsup, S.; Suthikeeree, W. (Dec 2010). "Wall thickness and outer diameter of the normal appendix in adults using 64 slices multidetector CT.". J Med Assoc Thai 93 (12): 1437-42. PMID 21344807.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Wiebe, BM. (Mar 1991). "Appendicitis and Enterobius vermicularis.". Scand J Gastroenterol 26 (3): 336-8. PMID 1853157.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Dahlstrom, JE.; Macarthur, EB. (Oct 1994). "Enterobius vermicularis: a possible cause of symptoms resembling appendicitis.". Aust N Z J Surg 64 (10): 692-4. PMID 7945067.
- ↑ Ariyarathenam AV, Nachimuthu S, Tang TY, Courtney ED, Harris SA, Harris AM (2010). "Enterobius vermicularis infestation of the appendix and management at the time of laparoscopic appendectomy: case series and literature review". Int J Surg 8 (6): 466–9. doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2010.06.007. PMID 20637320.
- ↑ URL: http://www.medilexicon.com/medicaldictionary.php?t=66889. Accessed on: 1 June 2011.
- ↑ Fink, AS.; Kosakowski, CA.; Hiatt, JR.; Cochran, AJ. (Jun 1990). "Periappendicitis is a significant clinical finding.". Am J Surg 159 (6): 564-8. PMID 2349982.
- ↑ O'Neil, MB.; Moore, DB. (Sep 1977). "Periappendicitis: Clinical reality or pathologic curiosity?". Am J Surg 134 (3): 356-7. PMID 900337.