Difference between revisions of "Graft-versus-host disease"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (5 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
Clinical: | Clinical: | ||
*May present as diarrhea. | *May present as diarrhea. | ||
*Main DDx (clinical): infection | *Main DDx (clinical): infection and certain drugs, especially mycophenolate | ||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
*Neutrophils | *Neutrophils may be present. | ||
DDx: | |||
* | *Drug effect (mycophenolate mofetil) - cannot be distinguished from GVHD. | ||
====Grading<ref name=pmid20953169/>==== | ====Grading<ref name=pmid20953169/>==== | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
===Microscopic (liver)=== | ===Microscopic (liver)=== | ||
:See: ''[[Vanishing bile duct syndrome]]''. | :See: ''[[Vanishing bile duct syndrome]]''. | ||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
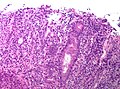
Image: apoptotic gastropathy intermed mag.jpg | Consistent with gastric GvHD (need to exclude mycophenolate as an alternative cause) - intermed mag. (WC) | |||
Image: apoptotic gastropathy high mag.jpg | Consistent with gastric GvHD - high mag. (WC) | |||
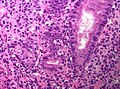
Image: Colonic graft-versus-host disease (high magnification).jpg | Colonic GvHD - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Skin graft versus host disease high mag 1.jpg | Skin GvHD - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Skin graft versus host disease high mag 1.jpg | Skin GvHD - high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
*[https://www.nature.com/articles/modpathol2010163/figures/1 GVHD grade 1-4 (nature.com)].<ref name=pmid20953169/> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 19:03, 11 February 2021
Graft-versus-host disease, abbreviated as GVHD, is a rare thingy seen mostly in tertiary care centres. It is a complication of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
General
- Complication of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, i.e. bone marrow transplantation (BMT).
- The histology of GVHD in the intestine is the same as rejection in bowel transplantation.[3]
Clinical:
- May present as diarrhea.
- Main DDx (clinical): infection and certain drugs, especially mycophenolate
Microscopic
Microscopic (skin)
Features:[4]
- Keratinocyte apoptosis.
- Intensely eosinophilic on H&E.
- Epidermotropic lymphocytic infiltrate = lymphocytes in the epidermis.
- Vacuolar degeneration of basal and suprabasal cells in the epidermis.
Note:
- Apoptotic cells should not be confused with dyskeratotic cells.[5]
Grading[4]
- Grade I: Only vacuolar changes, no apoptosis, no lymphocytes; not treated.
- Grade II: Only scattered apoptotic cells.
- Grade III: Focal separation/cleft formation at the dermal-epidermal junction.
- Grade IV: Extensive necrosis with degeneration of epidermis.
Notes:
- Same scheme applies to esophagus... it has the same structure.
- Originally described in NEJM.[6]
Microscopic (intestine)
Features:[7]
- Isolated epithelial cell apoptosis - key feature.
- +/-Crypt destruction (focal or extensive).
- +/-Loss of epithelium (denudation).
Notes:
- Neutrophils may be present.
DDx:
- Drug effect (mycophenolate mofetil) - cannot be distinguished from GVHD.
Grading[7]
- Grade 1 = isolated epithelial cell apoptosis.
- No crypt loss/destruction.
- Grade 2 = individual crypts are lost/scatter destruction of single crypts.
- Grade 3 = foci several adjacent crypts lost.
- Grade 4 = large number of adjacent crypts lost/loss of epithelium.
Notes:
- Low-grade rejection is a diagnosis that requires a careful examination, i.e. it is subtle.
Microscopic (liver)
Images
See also
References
- ↑ Niino D, Nakashima M, Kondo H, et al. (2005). "Correlation of donor-derived keratinocytes and severity of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) in epidermis". Pathol. Res. Pract. 200 (11-12): 775–81. PMID 15792120.
- ↑ van Dijk AM, Kessler FL, Verdonck LF, et al. (December 2000). "Primary human keratinocytes as targets in predicting acute graft-versus-host disease following HLA-identical bone marrow transplantation". Br. J. Haematol. 111 (3): 791–6. PMID 11122139.
- ↑ GT. 14 January 2011.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Acute Graft versus Host Disease of the Skin". http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/transplant/skinacutegvhd/printable.html. Retrieved January 17, 2011.
- ↑ Judith S. Nimmo. "Dyskeratotic, apoptotic or acantholytic keratinocytes? How to differentiate these on histology and what meaning does this have to the disease in question". http://dermatology.acvsc.org.au/dermatology_assets/documents/proc2007/acvs%20dermatology%20chapter%20proceedings%202007%20-%20nimmo%20-%20dyskeratotic,%20apoptotic%20or%20acantholytic%20keratinocytes.pdf. Retrieved 17 January 2011.
- ↑ Thomas ED, Storb R, Clift RA, et al. (April 1975). "Bone-marrow transplantation (second of two parts)". N. Engl. J. Med. 292 (17): 895–902. doi:10.1056/NEJM197504242921706. PMID 235092.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Cogbill CH, Drobyski WR, Komorowski RA (January 2011). "Gastrointestinal pathology of autologous graft-versus-host disease following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a clinicopathological study of 17 cases". Mod. Pathol. 24 (1): 117–25. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2010.163. PMID 20953169. http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v24/n1/full/modpathol2010163a.htm.