Difference between revisions of "Pediatric pathology"
(→Angelmann syndrome: more, refs) |
|||
| (37 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
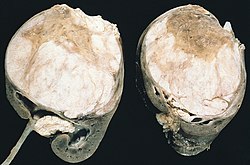
[[Image:Wilms tumor.jpg|thumb|right|250px|[[Gross pathology|Gross]] image of a [[Wilms tumour]], a tumour common in pediatric pathology. (WC/AFIP)]] | |||
The article deals with '''paediatric pathology''', which is quite different than adult pathology. Many diseases that afflict children are uncommon or unheard of in adults. | The article deals with '''paediatric pathology''', which is quite different than adult pathology. Many diseases that afflict children are uncommon or unheard of in adults. | ||
=Syndromes= | =Syndromes= | ||
==DiGeorge syndrome== | |||
{{Main|DiGeorge syndrome}} | |||
==Noonan syndrome== | ==Noonan syndrome== | ||
*Many different problems.<ref> | *Many different problems.<ref name=omim163950>{{OMIM|163950}}</ref> | ||
*Mutation in ''PTPN11 gene''. | |||
**This gene is also implicated in multiple [[granular cell tumour]]s. | |||
===Cardiac=== | ===Cardiac=== | ||
*May be associated with [[cardiomyopathy]]: DCM, RCM. | *May be associated with [[cardiomyopathy]]: [[DCM]], [[RCM]]. | ||
==Angelmann syndrome== | ==Angelmann syndrome== | ||
| Line 20: | Line 25: | ||
=Gastrointestinal pathology= | =Gastrointestinal pathology= | ||
{{Main|Pediatric gastrointestinal pathology}} | |||
GI is a big part pediatric pathology and therefore gets its own article. | |||
Among others, things discussed include: | |||
*[[Cystic fibrosis]]. | |||
* | *[[Aganglionosis]] (Hirschsprung disease). | ||
*[[Meconium peritonitis]]. | |||
*[[Necrotizing enterocolitis]]. | |||
=Pulmonary pathology= | |||
*'' | ==Respiratory distress syndrome== | ||
*Abbreviated ''RDS''. | |||
**Should not be confused with ''[[acute respiratory distress syndrome]]'' (ARDS). | |||
*Previously known as ''hyaline membrane disease''. | |||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
* | Associations: | ||
* | *Prematurity. | ||
*Maternal diabetes.<ref name=pmid22094826>{{Cite journal | last1 = Hay | first1 = WW. | title = Care of the Infant of the Diabetic Mother. | journal = Curr Diab Rep | volume = | issue = | pages = | month = Nov | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1007/s11892-011-0243-6 | PMID = 22094826 }}</ref> | |||
Etiology: | |||
* | *Not enough lung surfactant -> alveolar collapse with exhalation -> increased work of breathing. | ||
Complications of oxygen therapy:<ref name=Ref_PCPBoD8_244>{{Ref PCPBoD8|244}}</ref> | |||
*Retinopathy of prematurity. | |||
*[[Bronchopulmonary dysplasia]]. | |||
===Microscopic=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Features:<ref name= | Features:<ref name=Ref_PCPBoD8_243>{{Ref PCPBoD8|243}}</ref> | ||
* | *Proteineous (cellular) debris (hyaline membranes) line alveoli and respiratory bronchioles. | ||
Note: | |||
*Similar to ''[[diffuse alveolar damage]]''. | |||
* | |||
=Cardiovascular pathology= | |||
==Congenital heart disease== | |||
{{Main|Congenital heart disease}} | |||
This is a huge topic. | |||
== | |||
==Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn== | ==Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn== | ||
*Abbreviated PPHN. | *Abbreviated PPHN. | ||
| Line 136: | Line 101: | ||
White matter lesions:<ref name=pmid20626887/> | White matter lesions:<ref name=pmid20626887/> | ||
*Periventricular leukomalacia. | *[[Periventricular leukomalacia]]. | ||
*Subcortical leukomalacia. | *Subcortical leukomalacia. | ||
*Telencephalic (cerebral) leukomalacia. | *Telencephalic (cerebral) leukomalacia. | ||
| Line 149: | Line 114: | ||
***Image: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2799187/figure/F1/ Germinal matrix (nlm.nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid19816235/> | ***Image: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2799187/figure/F1/ Germinal matrix (nlm.nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid19816235/> | ||
*The germinal matrix is thought to be intrinsically fragile and is especially so in premature infants. | *The germinal matrix is thought to be intrinsically fragile and is especially so in premature infants. | ||
Grading: | |||
*Grade 1 = confined to germinal matrix. | |||
*Grade 2 = ventricular hemorrhage. | |||
*Grade 3 = distortion of ventricle. | |||
*Grade 4 = disruption of white matter. | |||
===Periventricular leukomalacia=== | |||
Features:<ref name=pmid12416551>{{Cite journal | last1 = Rezaie | first1 = P. | last2 = Dean | first2 = A. | title = Periventricular leukomalacia, inflammation and white matter lesions within the developing nervous system. | journal = Neuropathology | volume = 22 | issue = 3 | pages = 106-32 | month = Sep | year = 2002 | doi = | PMID = 12416551 }}</ref> | |||
*Multifocal [[necrosis]] of the cortical white matter adjacent to the lateral ventricles. | |||
*Usually symmetric. | |||
=Pediatric tumours= | |||
Many pediatric tumours have a "primative" histologic appearance and can be grouped into the category ''[[small round cell tumour]]'', which is covered in the article having that name and gives an overview of that grouping. | |||
==Wilms tumour== | |||
:[[AKA]] nephroblastoma. | |||
{{Main|Wilms tumour}} | |||
Most common abdominal solid organ malignancy in children. A good starting point if you're considering this entity is the ''[[small round cell tumours]]'' article. | |||
==Rhadomyosarcoma== | |||
:Commonly abbreviated ''RMS''. | |||
{{Main|Rhabdomyosarcoma}} | |||
This covers RMS. A good starting point if you're considering this entity is the ''[[small round cell tumours]]'' article. | |||
==Hepatoblastoma== | |||
{{Main|Hepatoblastoma}} | |||
A good starting point if you're considering this entity is the ''[[small round cell tumours]]'' article. | |||
==Lymphoma== | |||
{{Main|Lymphoma}} | |||
In reference to malignancies, these are very common in children. | |||
==Neuroblastoma== | |||
{{Main|Neuroblastoma}} | |||
A good starting point if you're considering this entity is the ''[[small round cell tumours]]'' article. | |||
=Dermatopathology= | |||
{{Main|Dermatopathology}} | |||
==Juvenile xanthogranuloma== | |||
{{Main|Juvenile xanthogranuloma}} | |||
=Soft tissue lesions= | |||
{{Main|Soft tissue lesions}} | |||
The histomorphology can look very malignant when viewed through the context of adult [[soft tissue pathology]].<ref>{{Ref PCPBoD8|252}}</ref> | |||
=References= | =References= | ||
| Line 165: | Line 175: | ||
*[http://www.sppg.ch/ Swiss pediatric pathology group (sppg.ch)]. | *[http://www.sppg.ch/ Swiss pediatric pathology group (sppg.ch)]. | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Pediatric pathology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 05:54, 12 January 2015
The article deals with paediatric pathology, which is quite different than adult pathology. Many diseases that afflict children are uncommon or unheard of in adults.
Syndromes
DiGeorge syndrome
Noonan syndrome
- Many different problems.[1]
- Mutation in PTPN11 gene.
- This gene is also implicated in multiple granular cell tumours.
Cardiac
- May be associated with cardiomyopathy: DCM, RCM.
Angelmann syndrome
- AKA happy puppet syndrome.
General
- Loss of a gene on 15q.
- May be due to genetic imprinting disorder, i.e. only maternal gene imprinting pattern is present (due to loss of the paternal chromosome).[2]
- Mental retardation.
Notes:
- Loss of the maternal imprinting pattern on 15q leads to Prader-Willi syndrome.[3]
Gastrointestinal pathology
GI is a big part pediatric pathology and therefore gets its own article.
Among others, things discussed include:
- Cystic fibrosis.
- Aganglionosis (Hirschsprung disease).
- Meconium peritonitis.
- Necrotizing enterocolitis.
Pulmonary pathology
Respiratory distress syndrome
- Abbreviated RDS.
- Should not be confused with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
- Previously known as hyaline membrane disease.
General
Associations:
- Prematurity.
- Maternal diabetes.[4]
Etiology:
- Not enough lung surfactant -> alveolar collapse with exhalation -> increased work of breathing.
Complications of oxygen therapy:[5]
- Retinopathy of prematurity.
- Bronchopulmonary dysplasia.
Microscopic
Features:[6]
- Proteineous (cellular) debris (hyaline membranes) line alveoli and respiratory bronchioles.
Note:
- Similar to diffuse alveolar damage.
Cardiovascular pathology
Congenital heart disease
This is a huge topic.
Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn
- Abbreviated PPHN.
- Related to patent ductus arteriosus and persistent fetal circulation.[7]
Associations:[8]
- Meconium aspiration.
- Anemia.
- Infection.
- Pneumonia (severe).
- Hypoglycemia.
- Birth asphyxia.
Williams syndrome
- Supravalvular stenosis.[9]
Neuropathology
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Abbreviated HIE.
General
- Autopsy adds some information.
- Two-tone liver - suggests prior injury.[10]
- HIE in perinatal period may be unique to the specific time of the injury, i.e. the type of hypoxic insults vary by developmental stage.[11]
- Some hypoxic injuries that are prenatal do not occur after birth.
- Pontosubicular necrosis is prenatal; the subiculum postnatal (like in adults) is resistant to hypoxic-ischemic insults.
- Hypoxic-ischemic insults are predominantly in the white matter. (???)
- Some hypoxic injuries that are prenatal do not occur after birth.
- HIE is the most common cause of neonatal seizures and often difficult to control with anticonvulsants.[12]
Possible findings in HIE
Hemorrhagic lesions:[13]
- Germinal matrix & intraventricular hemorrhage.
- Choroid plexus hemorrhage.
- Cerebellar hemorrhage.
- Subpial hemorrhage.
White matter lesions:[13]
- Periventricular leukomalacia.
- Subcortical leukomalacia.
- Telencephalic (cerebral) leukomalacia.
Grey matter lesions:[13]
- Pontosubicular necrosis.
- Infarcts of the cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, thalamus, brain stem.
Germinal matrix hemorrhage
- Arises from the germinal matrix, the tissue from which neurons and glial arise from.[14]
- Location: periventricular; may cause an intraventricular hemorrhage.
- The germinal matrix is thought to be intrinsically fragile and is especially so in premature infants.
Grading:
- Grade 1 = confined to germinal matrix.
- Grade 2 = ventricular hemorrhage.
- Grade 3 = distortion of ventricle.
- Grade 4 = disruption of white matter.
Periventricular leukomalacia
Features:[15]
- Multifocal necrosis of the cortical white matter adjacent to the lateral ventricles.
- Usually symmetric.
Pediatric tumours
Many pediatric tumours have a "primative" histologic appearance and can be grouped into the category small round cell tumour, which is covered in the article having that name and gives an overview of that grouping.
Wilms tumour
- AKA nephroblastoma.
Most common abdominal solid organ malignancy in children. A good starting point if you're considering this entity is the small round cell tumours article.
Rhadomyosarcoma
- Commonly abbreviated RMS.
This covers RMS. A good starting point if you're considering this entity is the small round cell tumours article.
Hepatoblastoma
A good starting point if you're considering this entity is the small round cell tumours article.
Lymphoma
In reference to malignancies, these are very common in children.
Neuroblastoma
A good starting point if you're considering this entity is the small round cell tumours article.
Dermatopathology
Juvenile xanthogranuloma
Soft tissue lesions
The histomorphology can look very malignant when viewed through the context of adult soft tissue pathology.[16]
References
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 163950
- ↑ URL: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/105830. Accessed on: 28 January 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/176270. Accessed on: 28 January 2011.
- ↑ Hay, WW. (Nov 2011). "Care of the Infant of the Diabetic Mother.". Curr Diab Rep. doi:10.1007/s11892-011-0243-6. PMID 22094826.
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 244. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 243. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ URL: http://www.thechildrenshospital.org/wellness/info/parents/20830.aspx. Accessed on: 4 January 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://www.thechildrenshospital.org/wellness/info/parents/20830.aspx. Accessed on: 4 January 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/194050. Accessed on: 11 January 2011.
- ↑ Elder DE, Zuccollo JM, Stanley TV (July 2005). "Neonatal death after hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy: does a postmortem add to the final diagnoses?". BJOG 112 (7): 935–40. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2005.00608.x. PMID 15957995.
- ↑ Grafe MR, Kinney HC (February 2002). "Neuropathology associated with stillbirth". Semin. Perinatol. 26 (1): 83–8. PMID 11876572.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/973501-overview. Accessed on: 7 January 2011.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 Riezzo I, Neri M, De Stefano F, et al. (2010). "The timing of perinatal hypoxia/ischemia events in term neonates: a retrospective autopsy study. HSPs, ORP-150 and COX2 are reliable markers to classify acute, perinatal events". Diagn Pathol 5: 49. doi:10.1186/1746-1596-5-49. PMC 2914029. PMID 20626887. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2914029/.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Ballabh P (January 2010). "Intraventricular hemorrhage in premature infants: mechanism of disease". Pediatr. Res. 67 (1): 1–8. doi:10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181c1b176. PMC 2799187. PMID 19816235. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2799187/.
- ↑ Rezaie, P.; Dean, A. (Sep 2002). "Periventricular leukomalacia, inflammation and white matter lesions within the developing nervous system.". Neuropathology 22 (3): 106-32. PMID 12416551.
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 252. ISBN 978-1416054542.