Difference between revisions of "Gastrointestinal tract polyps"
m (→Sign out) |
(redirect) |
||
| Line 457: | Line 457: | ||
==Traditional serrated adenoma== | ==Traditional serrated adenoma== | ||
{{Main|Traditional serrated adenoma}} | |||
==Sessile serrated adenoma== | ==Sessile serrated adenoma== | ||
{{Main|Sessile serrated adenoma}} | {{Main|Sessile serrated adenoma}} | ||
Revision as of 19:24, 9 July 2013
Gastrointestinal tract polyps, also gastrointestinal polyps or GI polyps, are the bread & butter of a GI pathologists workload. Some of 'em are benign... some pre-malignant... some malignant... some weird. Most GI polyps are from the intestine, i.e. intestinal polyps.
Overview - there are four basic types:[1]
- Hyperplastic - harmless, most common - 90% of all colonic polyps.[2]
- Hamartomatous - weriod stuff, syndromic things.
- Inflammatory - think inflammatory bowel disease, AKA pseudopolyps.
- Adenomatous - premalignant, several types (see below).
Mnemonic: HHI-A.
Diagnostic variability for colorectal polyps is substantial among community pathologists.[3]
Basic approach
- Sessile (flat) or polypoid (spherical, possibly has a stalk)?
- Nuclear features of adenoma & loss of goblets (hyperchromatic nuclei, nuclei round vs. flat, loss of nuclear stratification)?
- Inflammation?
- Serrated architecture?
A set of decision trees for GI polyps
Decision tree - GI polyps
| GI polyp | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Polypoid (Lollipop-like) | Sessile (flat) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nuclear changes | No nuc. change | Serrated | Not serrated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Polypoid adenoma (below) | Serrated | Not serrated | SSA vs. HP | Normal vs. VA | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HP | See misc. polyps (below) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Notes:
- Polypoid:
- Stalk visible (lollipop handle visible) or epithelial surface on three sides (or more).
- Sessile (flat):
- "Line of muscularis mucosa" visible +/- test tube-like intestinal crypts.
- Nuclear changes:
- Nuclear enlargement (elongation), crowding/pseudostratification, hyperchromasia (more blue) - especially at the surface, i.e. adjacent to the lumen (as opposed to the base of the crypt).
Decision tree - polypoid adenoma
| Polypoid adenoma | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serrated | Non-serrated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TSA | Tubular arch. | Tubulovillous arch. | Villous arch. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TA | TVA | VA | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Notes:[4]
- TA, tubular component >75%.
- VA, villous component >50%.
Decision tree - miscellaneous polyps
| Misc. polyps | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inflam. | No inflam. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Benign | Inflam. p. | Hamart. | Benign | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PJP | Juvenile | Other | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Notes:
- Juvenile polyps may have marked inflammation.
Hamartomatous polyps - basic DDx:
- Juvenile polyp/Retention polyp -- DIES (dilated glands, incr. LP, eroded surface, stalk).
- Peutz-Jeghers polyp (PJP) - frond-like with all mucosa components .
"Other" includes diagnoses which require history or tissue surround the polyp. These include the polyps seen in:
Tabular comparison of colonic polyps
Overview in two tables
Common colonic polyps
| Type | Key feature(s) | Details | Prevalence / prognosis | Other | DDx | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal mucosa / no pathology | test tubes in a rack-like morphology | small nuclei, abundant goblet cells | common / benign | moderate inflammation is normal | colonic spirochetes, cryptosporidiosis, microscopic colitis, CMV colitis | Normal - low mag. (ohio-state.edu) |
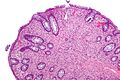
| Hyperplastic polyp | serrated at the surface | abundant goblet cells, usu. left colon; no features of SSA | common / benign | may be syndromic, e.g. hyperplastic polyposis syndrome | sessile serrated adenoma | |
| Traditional adenoma | nuclear hyperchromasia & pseudostratification / crowding at the luminal aspect | decreased goblet cells, usu. polypoid - on a stalk, usu. left colon | common / premalignant | tubular adenoma, tubulovillous adenoma, villous adenoma | traditional serrated adenoma, reactive changes (inflammation) |
Less common
| Type | Key feature(s) | Details | Prevalence / prognosis | Other | DDx | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sessile serrated adenoma (SSA) | basal crypt dilation & serration | boot-shaped crypts, horizontal crypts, branching crypts | uncommon / pre-malignant | AKA sessile serrated polyp | hyperplastic polyp | |
| Traditional serrated adenoma (TSA) | nuclear hyperchromasia & pseudostratification / crowding at the surface, serrated, villous-like architecture | decreased goblet cells | very rare / premalignant | called "traditional" to differentiate from SSA | traditional serrated adenoma (esp. villous adenoma) | |
| Juvenile polyp (retention polyp) | dilated glands, increased lamina propria | eroded surface (due to trauma), stalk (polypoid), inflammation - common | uncommon / benign if in isolation | may be part of juvenile polyposis syndrome | inflammatory pseudopolyp | |
| Inflammatory pseudopolyp | inflammation, erosion/ulceration adjacent to polyp | loss of mucosa adjacent to pseudopolyp | uncommon / seen in IBD, increased risk of malignancy | only seen in IBD; Dx implies IBD | juvenile polyp | Image |
| Peutz-Jeghers polyp (PJP) | branching smooth muscle | tree-like growth pattern | very rare / syndromic; assoc. with cancer | PJP not pre-malignant lesion in itself; see Peutz-Jeghers syndrome | normal, classically in the small bowel |
Common problems
Submucosal invasion
- This may be difficult to assess histomorphologically; these one should show a friend.
Pseudoinvasion
Early invasion
Adenomatous vs. hyperplastic
Adenomatous polyps & hyperplastic polyps - a comparison (adapted from Li and Burgart[5]):
| Attribute | Hyperplastic polyp (HP) | Sessile serrated adenoma (SSA) | Traditional serrated adenoma (TSA) | Traditional adenoma -tubular adenoma -tubulovillous adenoma -villous adenoma |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classic location | rectum/left colon | right colon | rectum/left colon | rectum/left colon |
| Morphology | polypoid | flat (sessile) | polypoid | polypoid |
| Cytologic atypia -Cigar nuclei -Hyperchromasia -Nuclear crowding |
absent | absent | present | present |
| Location of worst atypia | - | - | basal | luminal |
| Cytoplasm | eosinophilic | prominent eosinophilia | eosinophilic | basophilic |
| Goblet cells | abundant | common | less common | less common |
| Luminal Serration | present | common | present | absent |
| SSA architecture -Basal crypt serration -Basal crypt dilation -Horizonatal crypts -Branched crypts |
absent | present | absent | absent |
| Key feature(s) | serrated luminal surf. & goblets | abnorm. crypt arch. & sessile | nuclear atypia & serrated | nuclear atypia (luminal) |
| Image(s) |
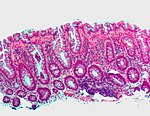
Normal colonic mucosa:
- Nuclei - round and basally located.
- Abundant goblet cells.
- Moderate inflammation.
- Paneth cells - present in right colon.
- Glands - straight, no branching; "test tube" shape.
Notes: Left colon refers to the sigmoid colon, descending colon and the distal half of the transverse colon; right colon refers to the cecum, ascending colon and proximal half of the transverse colon.
Normal
Normal colorectal mucosa
General
- Endoscopists go after anything that is polypoid... and that may be normal.
Microscopic
Features:
- Test tube like glands.
- Minimal palisading.
- Nuclei <3:1 = height:width.
- No nuclear pseudostratification. †
- Deep part of crypt is more hyperchromatic than superficial component - important.
- The surface should be lighter staining than the deeper aspect, i.e. the deeper glands are dark blue and the superficial gland are light blue.
Note:
- † May be seen in reactive changes.
DDx (colorectal mucosa with minimal changes):
Images
www:
- Normal colorectal mucosa (uwa.edu.au).[6]
- Colon (siumed.edu).
- Normal colorectal mucosa (maricopa.edu).
Sign out
Normal
SIGMOID COLON, BIOPSY: - COLORECTAL-TYPE MUCOSA WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS.
COLON, 70 CM, BIOPSY: - COLORECTAL-TYPE MUCOSA WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS.
Mucosa and submucosa
POLYP, SIGMOID COLON, BIOPSY: - COLONIC MUCOSA AND SUBMUCOSA WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS.
Lymphoid nodule present
POLYP, ASCENDING COLON, BIOPSY: - COLONIC MUCOSA AND SUBMUCOSA WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS WITH A MORPHOLOGICALLY BENIGN LYMPHOID NODULE.
Note:
- Lymphoid nodules manifest endoscopically as a small polypoid protuberances. It is worthwhile to report the presence of lymphoid nodules as they reassure the endoscopist that they probably sampled the abnormality they saw.
Suspected missed lesion
RECTOSIGMOID, BIOPSY: - COLORECTAL-TYPE MUCOSA WITH A LYMPHOID AGGREGATE. - NEGATIVE FOR ACTIVE COLITIS. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY -- SEE COMMENT. COMMENT: The clinical history is noted. This biopsy does not show neoplastic tissue; however, the biopsy may not be representative of the lesion seen. Levels were cut and these did not yield additional information. There are no changes to suggest a chronic colitis. Correlation with imaging may be useful. A re-biopsy is suggested.
Fecal material
- Fecal matter redirects here.
General
- Common.
- Associated with poor bowel preparation.
- Endoscopists go after anything that is polypoid and that may be nothing more than poo.
Microscopic
Features:
- Plant material:
- Yellow staining chicken wire-like material - may be linear.
- Thick cell walls often without cytoplasm and usually without a nucleus.
- Yellow staining chicken wire-like material - may be linear.
- Meat:
- Eosinophilic honeycomb-like material without nuclei and without inflammation.
- Essentially ischemic skeletal muscle without inflammation.
- Eosinophilic honeycomb-like material without nuclei and without inflammation.
- +/-Microorganisms.
- +/-Inflammatory cells.
DDx:
- Necrosis.
Sign out
TRANSVERSE COLON, BIOPSY: - FECAL MATERIAL. - NO DEFINITE COLONIC MUCOSA IDENTIFIED.
Rectum
RECTUM, BIOPSY: - FECAL MATERIAL. - NO DEFINITE RECTAL MUCOSA IDENTIFIED.
Hyperplastic polyp
- The stomach lesion is dealt with in hyperplastic polyp of the stomach.
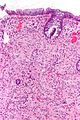
Inflammatory pseudopolyp
- AKA inflammatory polyp.
General
- Not a true polyp.
- The label inflammatory pseudopolyp = inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
- If there is no history of IBD... reconsider the diagnosis.
Microscopic
Features:
- Polypoid shape.
- Inflammation - esp. neutrophils - key feature.
Negatives:
- No nuclear atypia.
- May have focal nuclear hyperchromasia and nuclear enlargement.
- No dilated glands.
DDx:
Images:
Sign out
SIGMOID COLON POLYP, PERI-DIVERTICULAR, BIOPSY: - INFLAMMATORY PSEUDOPOLYP.
POLYP, DESCENDING COLON, BIOPSY: - INFLAMED POLYPOID FRAGMENT OF COLORECTAL-TYPE MUCOSA. -- NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA.
Micro
The sections show a fragment of colorectal mucosa with focal ulceration, acute inflammation and a well-vascularized stroma with plump stromal cells. Occasional stromal cells have nuclear hyperchromasia.
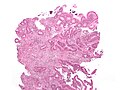
Adenomatous polyps
Overview
Several types of adenomatous polyps are recognized:
- Traditional adenomas (have three subtypes):
- Tubular adenoma - most common, lowest malignant potential.
- Tubulovillous adenoma.
- Villous adenoma - highest malignant potential.
- Sessile serrated adenomas:
- New kid on the block.
- Traditional serrated adenomas - nuclear features of 'traditional adenoma' + serrated architecture.
Notes:
- They are all considered pre-malignant, i.e. if you leave 'em in place they often develop into cancer.
- If multiple... think about familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), attenuated FAP, MUTYH polyposis syndrome, serrated polyposis syndrome.
Management of (adenomatous colonic) polyps
Follow-up interval for polyps (colonoscopy interval):[7]
- Normal follow-up (includes presence of hyperplastic polyps): ~10 years.
- 1-2 low risk (adenomatous) polyps: 5-10 years.
- 3-10 low risk polyps or a high risk polyp: 3 years.
- >10 low risk polyps: <3 years.
- Inadequately removed polyps: <6 months.
Classified as high risk polyp (any of the following):[7]
- Tubulovillous.
- Villous.
- High grade dysplasia.
- Size >= 1 cm.
Mnemonic: GAS = grade (high), architecture (tubulovillous, villous), size (>1 cm).
Note:
- High risk polyp, as defined above, is also called advanced adenoma;[8] however, it should be noted that there are different definitions for advanced adenoma (e.g. Winawer & Zauber[9] include early invasive tumours). Thus, it is best to avoid the term.
Pseudoinvasion in colorectal adenomatous polyps
- AKA pseudoinvasion.
General
Microscopic
Features - classic:[12]
- Dysplastic glands surrounded by lamina propria.
- Hemosiderin.
- Lack of desmoplastic reaction.
- +/-Cystic spaces with rounded contours without cells floating in them.
Memory device (classic features) LDH:
- Lamina propria.
- Desmoplasia lacking.
- Hemosiderin.
DDx:
Sign out
COLON POLYP, SIGMOID COLON AT 45 CM, EXCISION: - TUBULAR ADENOMA. -- NEGATIVE FOR HIGH-GRADE DYSPLASIA. - SUBMUCOSA PRESENT, NO EVIDENCE OF INVASION. - ABUNDANT HEMOSIDERIN-LADEN MACROPHAGES.
High-risk features in (colorectal) adenomatous polyps with carcinoma
Predictors of poor outcome with early submucosal invasion:[13]
- High tumour grade.
- Lymphovascular invasion.
- High-grade tumour budding.
- Tumour bud = 1-4 cell(s); "high-grade budding" is >=10 tumour buds in a field of 0.385 mm2.[14]
- If the microscope has a 22 mm eye piece and...
- A 20x objective, the field is approximately 0.950 mm2 -- to match the area/bud -- it would be 24.68 buds/0.950 mm2.
- A 40x objective, the field is approximately 0.238 mm2 -- to match the area/bud -- it would be 6.17 buds/0.238 mm2.
- If the microscope has a 22 mm eye piece and...
- Tumour bud = 1-4 cell(s); "high-grade budding" is >=10 tumour buds in a field of 0.385 mm2.[14]
- Extensive submucosal invasion.
- >= 4 mm width or >= 2 mm depth.
If none of the above factors is present the risk of lymph node metastasis is < 1%. The presence of one risk factor increases the risk to ~20%. If multiple risk factors are present the chance of lymph node metastases is greater than 35%.[13]
Traditional adenoma
- Includes tubular adenoma, tubulovillous adenoma, and villous adenoma.
Traditional serrated adenoma
Sessile serrated adenoma
Malignant polyps
Colorectal adenocarcinoma
General
- Diagnosis may be a challenging on a small biopsy.
Clinical
Invasion can be predicted based on endoscopic findings:
- Kudo pit pattern.[15]
- Non-lifting sign.[16]
- Presence predicts deeper invasion.[17]
Microscopic
One of the two following:
- Dysplasia and evidence of invasion - features:[18]
- Nuclear changes seen in adenomatous polyps - malignant-appearing cells.
- Enlarged nuclei.
- Chromatin hyperchromatic or vesicular.
- Round-shape or cigar-shaped and pseudostratified.
- Architectural changes - usually those of high-grade dysplasia:
- Cribriforming - most common.
- Papillary tufting.
- Budding.
- Sheeting.
- Deep involvement - one of the two following - key feature:
- Malignant-appearing cells in the submucosa.
- Pseudoinvasion must be excluded.
- Desmoplastic stromal response.
- Spindle cells with:
- Large nuclei (nucleus ~ size of a plasma cell).
- Eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- Spindle cells with:
- Malignant-appearing cells in the submucosa.
- Nuclear changes seen in adenomatous polyps - malignant-appearing cells.
- Signet ring cells.
DDx:
- Pseudoinvasion - surrounded by lamina propria, desmoplasia lacking, hemosiderin-laden macrophages.
- Reactive changes.
Note:
- Desmoplastic response is not predictive of submucosal invasion in pedunculated polyps.[19]
Image
Sign out
RECTOSIGMOID TUMOUR, BIOPSY: - INVASIVE ADENOCARCINOMA, MODERATELY DIFFERENTIATED.
Micro
The sections shows colorectal-type mucosa with a tubule-forming epithelium that has cellular pseudostratification and enlarged hyperchromatic nuclei, from the crypt base to the luminal aspect (dysplasia).
There is cribriforming of glands and epithelial budding. Plump spindle cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm surround the abnormal epithelium (desmoplastic stroma). No definite submucosa is identified; the diagnosis is based on the stromal desmoplasia.
Hamartomatous polyps
Overview
There are three well known hamartomatous polyp syndromes:[20]
There are two obscure hamartomatous polyp syndromes:[20]
- Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome (BRBS).
- Devon polyposis syndrome (DPS).
Notes:
- BRBS is due to a PTEN mutation[21] (the same gene associated with Cowden's disease).
- DPS is reported in only one family that lives in Devon, UK.[22]
Juvenile polyp
- AKA retention polyp in adults.
General
May be part of a syndrome:
- Juvenile polyposis syndrome (JPS) - see JPS article for criteria.
- Cronkhite-Canada syndrome.
- Cowden syndrome.
Gross
- Mushroom-like shape.
Microscopic
- Eroded, smooth or lobulated surface.
- Pedunculated.
- Increased lamina propria (LP) +/- edema.
- Cystically dilated gland.
- Often inflammed.
Mnemonic DIES = dilated glands, increased LP & inflammation of the LP, eroded/smooth surface, stalk.
Notes:
- May have nuclear changes like those seen in adenomatous polyps.
DDx:
- Inflammatory polyp.
- Hyperplastic polyp of the stomach - less lamina propria, foveolar hyperplasia (long tortuous glands).
- Cronkhite-Canada syndrome - have changes in the surrounding mucosa, clinical findings (nail atrophy, skin pigment, alopecia).
Images
www:
IHC
- Usually none.
Notes:
- IHC can be used if it is suspected to have dysplasia (p53, Ki-67).
- p53 mutations in dysplastic epithelium -- negative stain (normal).
Sign out
RECTOSIGMOID POLYP, BIOPSY: - RETENTION POLYP.
Peutz-Jeghers polyp
General
Epidemiology
- Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is autosomal dominant.
- Altered gene: STK11.
Clinical
Features:[25]
- Melanocytic macules.
- Lips, buccal mucosa, and digits.
- Multiple Peutz-Jeghers polyps.
Increased risk of various neoplasms - primarily:
- Breast and gastrointestinal cancer.[26]
- Others tumours:[27]
- Granulosa cell tumour.
- Sertoli cell tumour - esp. with calcification.
Microscopic
- Frond-like polyp with all three components of mucosa:
- Muscosal epithelium (melanotic mucosa, goblet cells).
- Lamina propria.
- M. mucosae.
Notes:
- Frond = leaflike expansion.[28]
- The key is "thick" smooth muscle bundles - if one is lucky one sees branching.[29]
- "Thick" ~= thickness of muscularis mucosae.
- The key is "thick" smooth muscle bundles - if one is lucky one sees branching.[29]
Images
www:
Sign out
Duodenum
POLYPS, DUODENUM, EXCISION: - PEUTZ-JEGHERS POLYPS (x2) WITH BRUNNER'S GLANDS. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Colon
POLYP, COLON (40 CM), EXCISION: - PEUTZ-JEGHERS POLYP. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Cowden disease
- AKA Cowden syndrome.
General
Etiology:
- PTEN gene mutation.
Clinical features:[30]
- Hamartomatous polyps.
- Facial trichilemmomas (hair follicle root sheath epithelium tumour).
- Oral papillomas.
- Acral keratoses (peripheral keratoses).
Note:
- Lame mnemonic PATH:[31] Papilloma (oral), Acral keratosis, Trichilemmoma, Hamartomatous polyps.
Microscopic
Features:
- Hamartomatous polyp - features non-specific. (???)
Weird stuff
Cronkhite-Canada syndrome
- Abbreviated CCS.
General
Clinical features:[32]
- Hamartomatous polyps.
- Ectodermal abnormalities (nail atrophy, skin pigment, alopecia).
Microscopic
Features:
- Polyps have same morphology as juvenile polyps/retension polyps.
- Crypt dilation and edema in non-polypoid mucosa[33] - key feature.
DDx:
Images:
Ganglioneuroma
General
- May be part of MEN 2B.
Microscopic
Features - see ganglioneuroma:
- Ganglion cells - key feature.
- Large cells with a round nucleus and a prominent nucleolus.
Images
Inflammatory myoglandular polyp
General
- Controversial - probably not a distinct pathologic entity.[34]
- Rare, benign, non-neoplastic.[35]
- Large bowel, usually rectosigmoid.
Microscopic
Features:[36]
- Granulation tissue within the lamina propria.
- Lamina propria smooth muscle.
- Irregular gland architecture:
- Cystic dilatation.
- Tortuosity.
DDx:[34]
- Mucosal prolapse syndrome.
- Polypoid prolaping mucosal fold in diverticular disease.
- Inflammatory cloacogenic polyp.
- Inflammatory cap polyp.
Image:
See also
References
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 856. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 858. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ Rex, DK.; Alikhan, M.; Cummings, O.; Ulbright, TM. (Oct 1999). "Accuracy of pathologic interpretation of colorectal polyps by general pathologists in community practice.". Gastrointest Endosc 50 (4): 468-74. PMID 10502165.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 860. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ Li SC, Burgart L (March 2007). "Histopathology of serrated adenoma, its variants, and differentiation from conventional adenomatous and hyperplastic polyps". Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 131 (3): 440-5. PMID 17516746. http://journals.allenpress.com/jrnlserv/?request=get-abstract&issn=0003-9985&volume=131&page=440.
- ↑ URL: http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/CorePages/GIT/git.htm. Accessed on: 18 October 2012.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Levine JS, Ahnen DJ (December 2006). "Clinical practice. Adenomatous polyps of the colon". N. Engl. J. Med. 355 (24): 2551–7. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp063038. PMID 17167138. http://content.nejm.org/cgi/reprint/355/24/2551.pdf.
- ↑ Laiyemo, AO.; Murphy, G.; Albert, PS.; Sansbury, LB.; Wang, Z.; Cross, AJ.; Marcus, PM.; Caan, B. et al. (Mar 2008). "Postpolypectomy colonoscopy surveillance guidelines: predictive accuracy for advanced adenoma at 4 years.". Ann Intern Med 148 (6): 419-26. PMID 18347350.
- ↑ Winawer, SJ.; Zauber, AG. (Jan 2002). "The advanced adenoma as the primary target of screening.". Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 12 (1): 1-9, v. PMID 11916153.
- ↑ Byun, TJ.; Han, DS.; Ahn, SB.; Cho, HS.; Eun, CS.; Jeon, YC.; Sohn, JH.; Oh, YH. (Jun 2009). "Pseudoinvasion in an adenomatous polyp of the colon mimicking invasive colon cancer.". Gut Liver 3 (2): 130-3. doi:10.5009/gnl.2009.3.2.130. PMC PMC2852693. PMID 20431736. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMCPMC2852693/.
- ↑ Odze, Robert D.; Goldblum, John R. (2009). Surgical pathology of the GI tract, liver, biliary tract and pancreas (2nd ed.). Saunders. pp. 512. ISBN 978-1416040590.
- ↑ Muto, T.; Bussey, HJ.; Morson, BC. (Jan 1973). "Pseudo-carcinomatous invasion in adenomatous polyps of the colon and rectum.". J Clin Pathol 26 (1): 25-31. PMC 477644. PMID 4540378. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC477644/.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Ueno, H.; Mochizuki, H.; Hashiguchi, Y.; Shimazaki, H.; Aida, S.; Hase, K.; Matsukuma, S.; Kanai, T. et al. (Aug 2004). "Risk factors for an adverse outcome in early invasive colorectal carcinoma.". Gastroenterology 127 (2): 385-94. PMID 15300569.
- ↑ Ueno, H.; Murphy, J.; Jass, JR.; Mochizuki, H.; Talbot, IC. (Feb 2002). "Tumour 'budding' as an index to estimate the potential of aggressiveness in rectal cancer.". Histopathology 40 (2): 127-32. PMID 11952856.
- ↑ Onishi, T.; Tamura, S.; Kuratani, Y.; Onishi, S.; Yasuda, N. (2008). "Evaluation of the depth score of type V pit patterns in crypt orifices of colorectal neoplastic lesions.". J Gastroenterol 43 (4): 291-7. doi:10.1007/s00535-008-2161-1. PMID 18458845.
- ↑ Uno, Y.; Munakata, A.. "The non-lifting sign of invasive colon cancer.". Gastrointest Endosc 40 (4): 485-9. PMID 7926542.
- ↑ Ishiguro, A.; Uno, Y.; Ishiguro, Y.; Munakata, A.; Morita, T. (Sep 1999). "Correlation of lifting versus non-lifting and microscopic depth of invasion in early colorectal cancer.". Gastrointest Endosc 50 (3): 329-33. doi:10.1053/ge.1999.v50.98591. PMID 10462651.
- ↑ Kimura, R.; Fujimori, T.; Ichikawa, K.; Ajioka, Y.; Ueno, H.; Ohkura, Y.; Kashida, H.; Togashi, K. et al. (Aug 2012). "Desmoplastic reaction in biopsy specimens of early colorectal cancer: a Japanese prospective multicenter study.". Pathol Int 62 (8): 525-31. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1827.2012.02840.x. PMID 22827760.
- ↑ Hirose, M.; Fukui, H.; Igarashi, Y.; Fujimori, Y.; Katake, Y.; Sekikawa, A.; Ichikawa, K.; Tomita, S. et al. (Dec 2010). "Detection of desmoplastic reaction in biopsy specimens is useful for predicting the depth of invasion of early colorectal cancer: a Japanese collaborative study.". J Gastroenterol 45 (12): 1212-8. doi:10.1007/s00535-010-0288-3. PMID 20665053.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Iacobuzio-Donahue, Christine A.; Montgomery, Elizabeth A. (2005). Gastrointestinal and Liver Pathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 345. ISBN 978-0443066573.
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 153480
- ↑ Allibone, RO.; Nanson, JK.; Anthony, PP. (Jul 1992). "Multiple and recurrent inflammatory fibroid polyps in a Devon family ('Devon polyposis syndrome'): an update.". Gut 33 (7): 1004-5. PMID 1644320.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 23.2 Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 859. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 24.2 Bronner, MP. (Apr 2003). "Gastrointestinal inherited polyposis syndromes.". Mod Pathol 16 (4): 359-65. doi:10.1097/01.MP.0000062992.54036.E4. PMID 12692201. http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v16/n4/full/3880773a.html.
- ↑ URL: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/175200. Accessed on: 13 July 2010.
- ↑ Beggs AD, Latchford AR, Vasen HF, et al. (July 2010). "Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: a systematic review and recommendations for management". Gut 59 (7): 975–86. doi:10.1136/gut.2009.198499. PMID 20581245.
- ↑ URL: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/175200. Accessed on: 22 December 2010.
- ↑ URL: http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/frond. Accessed on: 26 July 2011.
- ↑ C. Streutker. 26 July 2011.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 858-9. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ URL: http://www.pathologyexpert.com/boards/onlinefiles/syndromes.htm. Accessed on: 6 December 2011.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 858-9. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 430. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 Bhathal, PS.; Chetty, R.; Slavin, JL. (Aug 1993). "Myoglandular polyps.". Am J Surg Pathol 17 (8): 852-3. PMID 8338196.
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 Meniconi, RL.; Caronna, R.; Benedetti, M.; Fanello, G.; Ciardi, A.; Schiratti, M.; Papini, F.; Farelli, F. et al. (2010). "Inflammatory myoglandular polyp of the cecum: case report and review of literature.". BMC Gastroenterol 10: 10. doi:10.1186/1471-230X-10-10. PMC 2828397. PMID 20102635. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2828397/.
- ↑ Nakamura, S.; Kino, I.; Akagi, T. (Aug 1992). "Inflammatory myoglandular polyps of the colon and rectum. A clinicopathological study of 32 pedunculated polyps, distinct from other types of polyps.". Am J Surg Pathol 16 (8): 772-9. PMID 1309176.
External links
- Serrated polyps quiz (unibas.ch) - nice quiz... though it is annoying that one has to click on the images to enlarge 'em.