Difference between revisions of "Keloid"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(split-out) |
(→References: fix ref) |
||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist| | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Dermatopathology]] | [[Category:Dermatopathology]] | ||
Revision as of 22:29, 21 August 2013
| Keloid | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
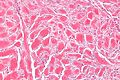
 Keloid. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | thick collagen bundles - surrounded by paler staining fibroblasts, loss of adnexal structures |
| LM DDx | hypertrophic scar |
| Site | skin |
|
| |
| Clinical history | typically dark skinned individuals |
| Prognosis | benign |
- Hypertrophic scar redirects here.
Keloid is an uncommon abnormal scarring.
General
- Sites of previous trauma/surgery, esp. in dark skinned individuals.[1]
Note:
- Reported as "keloidal-type collagen"; the clinician decides between hypertrophic scar and keloid.
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Thick collagen bundles - surrounded by paler staining fibroblasts - key feature.
- Lesion replaces adnexal structures, e.g. hair, sweat glands.
DDx:
- Hypertrophic scar.[2]
Images
www:
Sign out
SKIN LESION, LEFT SCAPULA, EXCISION: - DERMAL SCAR WITH KELOIDAL-TYPE COLLAGEN, SEE COMMENT. COMMENT: The findings are consistent with a hypertrophic scar or keloid; clinical correlation is required.
Clinical provided
SKIN LESION, LEFT NIPPLE AREOLA, EXCISION: - DERMAL SCAR WITH KELOIDAL-TYPE COLLAGEN, CONSISTENT WITH HYPERTROPHIC SCAR.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 492. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Gauglitz, GG.; Korting, HC.; Pavicic, T.; Ruzicka, T.; Jeschke, MG.. "Hypertrophic scarring and keloids: pathomechanisms and current and emerging treatment strategies.". Mol Med 17 (1-2): 113-25. doi:10.2119/molmed.2009.00153. PMC 3022978. PMID 20927486. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3022978/.