Difference between revisions of "Nipple adenoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
*Not encapsulated.<ref name=pmid2123505/> | |||
*Proliferation of epithelial and myoepithelial elements that extends into the breast stroma.<ref name=pmid2123505>{{Cite journal | title = Adenoma of Nipple. | journal = Br Med J | volume = 1 | issue = 5330 | pages = 563 | month = Mar | year = 1963 | doi = | PMID = 20789667 | PMC = 2123505 | url = http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2123505/?page=1 }}</ref> | *Proliferation of epithelial and myoepithelial elements that extends into the breast stroma.<ref name=pmid2123505>{{Cite journal | title = Adenoma of Nipple. | journal = Br Med J | volume = 1 | issue = 5330 | pages = 563 | month = Mar | year = 1963 | doi = | PMID = 20789667 | PMC = 2123505 | url = http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2123505/?page=1 }}</ref> | ||
*Arborising papillomatous epithelial proliferation within duct | *Arborising papillomatous epithelial proliferation within duct | ||
*Papillae have fibrovascular cores. | *(Papillae have fibrovascular cores) at least as far as I can see but not according to Stanford. | ||
*Florid epithelial hyperplasia can be seen | *Florid epithelial hyperplasia can be seen | ||
*Can see haphazard arrangement of proliferating tubular structures | *Can see haphazard arrangement of proliferating tubular structures | ||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
*Lacks true fibrovascular cores.<ref>URL: [http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/breast/nippleadenoma/printable.html http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/breast/nippleadenoma/printable.html]. Accessed on: 6 August 2011.</ref> | *Lacks true fibrovascular cores.<ref>URL: [http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/breast/nippleadenoma/printable.html http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/breast/nippleadenoma/printable.html]. Accessed on: 6 August 2011.</ref> | ||
*Focal necrosis may be present.<ref name=Ref_APBR307>{{Ref APBR|307 Q16}}</ref> | *Focal necrosis may be present.<ref name=Ref_APBR307>{{Ref APBR|307 Q16}}</ref> | ||
| Line 61: | Line 60: | ||
**Often deeper - one should '''not''' see skin in the histologic section. | **Often deeper - one should '''not''' see skin in the histologic section. | ||
*Syringomatous adenoma | *Syringomatous adenoma | ||
*Intraductal carcinoma - | *Intraductal carcinoma - the proliferation in nipple adenoma should be no more atypical than that seen with usual intraductal hyperplasia or intraductal papillomatosis. Cribriforming glands should be absent | ||
*Invasive ductal carcinoma - IHC is useful (see below) the ducts should all be lined by myoepithelium. | *Invasive ductal carcinoma - IHC is useful (see below) the ducts should all be lined by myoepithelium. | ||
Revision as of 10:47, 26 March 2015
| Nipple adenoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
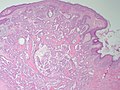
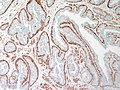
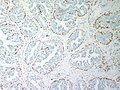
 Nipple adenoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | proliferation of epithelial and myoepithelial elements that extends into the breast stroma; not encapsulated; lacks true fibrovascular cores, +/-focal necrosis |
| LM DDx | intraductal papilloma |
| Site | breast - nipple |
|
| |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | Paget's disease of the breast |
Nipple adenoma is a benign pathology of the breast.
It is also known as nipple duct adenoma, nipple adenoma of breast, adenoma of the nipple and florid papillomatosis of the nipple.[1]
General
Clinical DDx:
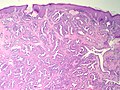
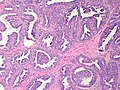
Microscopic
Features:
- Not encapsulated.[4]
- Proliferation of epithelial and myoepithelial elements that extends into the breast stroma.[4]
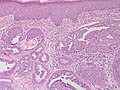
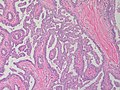
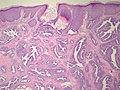
- Arborising papillomatous epithelial proliferation within duct
- (Papillae have fibrovascular cores) at least as far as I can see but not according to Stanford.
- Florid epithelial hyperplasia can be seen
- Can see haphazard arrangement of proliferating tubular structures
Notes:
DDx:
- Intraductal papilloma.
- Found within the duct not the stroma.
- Often deeper - one should not see skin in the histologic section.
- Syringomatous adenoma
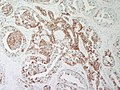
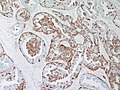
- Intraductal carcinoma - the proliferation in nipple adenoma should be no more atypical than that seen with usual intraductal hyperplasia or intraductal papillomatosis. Cribriforming glands should be absent
- Invasive ductal carcinoma - IHC is useful (see below) the ducts should all be lined by myoepithelium.
Images
www:
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Boutayeb, S.; Benomar, S.; Sbitti, Y.; Harroudi, T.; Hassam, B.; Errihani, H. (2012). "Nipple adenoma in a man: An unusual case report.". Int J Surg Case Rep 3 (5): 190-2. doi:10.1016/j.ijscr.2011.05.008. PMID 22342578.
- ↑ Shinn, L.; Woodward, C.; Boddu, S.; Jha, P.; Fouroutan, H.; Péley, G.. "Nipple adenoma arising in a supernumerary mammary gland: a case report.". Tumori 97 (6): 812-4. doi:10.1700/1018.11102. PMID 22322852.
- ↑ HANDLEY, RS.; THACKRAY, AC. (Jun 1962). "Adenoma of nipple.". Br J Cancer 16: 187-94. PMC 2070922. PMID 13904317. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2070922/?tool=pubmed.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Adenoma of Nipple.". Br Med J 1 (5330): 563. Mar 1963. PMC 2123505. PMID 20789667. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2123505/?page=1.
- ↑ URL: http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/breast/nippleadenoma/printable.html. Accessed on: 6 August 2011.
- ↑ Lefkowitch, Jay H. (2006). Anatomic Pathology Board Review (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 307 Q16. ISBN 978-1416025887.