Difference between revisions of "Seminoma"
(+cat.) |
(split-out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
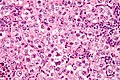
| Image = Seminoma_high_mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Seminoma. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Micro = fried egg-like cells (clear or eosinophilic cytoplasm, central nucleus), lymphocytic infiltrate (common), +/-[[syncytiotrophoblast]]s (rare), +/-granulomas (uncommon) | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = [[embryonal carcinoma]], [[ITGCN]], [[mixed germ cell tumour]], granulomatous orchitis | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = OCT3/4 +ve, PLAP +ve, D2-40 +ve, CD30 -ve | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[testis]] | |||
| Assdx = [[ITGCN]] | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = testicular mass, +/-retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = | |||
| Bloodwork = +/-beta-hCG elevated | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = good | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = other [[testis|testicular tumours]] ([[germ cell tumour]]s, [[lymphoma) | |||
}} | |||
'''Seminoma''' is a common [[testis|testicular]] [[germ cell tumour]]. | |||
It should ''not'' be confused with the unrelated tumour called ''[[spermatocytic seminoma]]''. | |||
===General=== | |||
*Male counterpart of the [[dysgerminoma]], which arise in the [[ovary]]. | |||
*Most common [[germ cell tumour]] of the testis. | |||
Clinical: | |||
*Elevated serum LDH. | |||
*Normal serum alpha fetoprotein. | |||
*Usually normal beta-hCG. | |||
Note: | |||
*Rarely, it may present a retroperitoneal mass.<ref name=pmid21424055>{{Cite journal | last1 = Preda | first1 = O. | last2 = Nicolae | first2 = A. | last3 = Loghin | first3 = A. | last4 = Borda | first4 = A. | last5 = Nogales | first5 = FF. | title = Retroperitoneal seminoma as a first manifestation of a partially regressed (burnt-out) testicular germ cell tumor. | journal = Rom J Morphol Embryol | volume = 52 | issue = 1 | pages = 193-6 | month = | year = 2011 | doi = | PMID = 21424055 }}</ref> | |||
====Epidemiology & etiology==== | |||
*Arises from ''[[intratubular germ cell neoplasia]]'' (ITGCN). | |||
===Microsopic=== | |||
Features: | |||
*Cells with fried egg appearance - '''key feature''': | |||
**Clear cytoplasm. | |||
**Central nucleus, with prominent nucleolus. | |||
***Nucleus may have "corners", i.e. it is ''not'' round. | |||
*+/-Lymphoctyes - interspersed (very common). | |||
*+/-[[Syncytiotrophoblast]]s, [[AKA]] ''syncytiotrophoblastic giant cells'' (STGCs),<ref name=Ref_GUP542>{{Ref GUP|542}}</ref> present in ~10-20% of seminoma.<ref>URL: [http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?case=31&n=10 http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?case=31&n=10]. Accessed on: 22 May 2012.</ref> | |||
**Large + irregular, vesicular nuclei. | |||
**Eosinophilic vacuolated cytoplasm (contains hCG). | |||
***Syncytiotrophoblasts = closest to mom in normal [[chorionic villi]] - covers cytotrophoblast.<ref>URL: [http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/45/Gray37.png http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/45/Gray37.png]. Accessed on: 31 May 2010.</ref> | |||
*+/-Florid granulomatous reaction. | |||
Memory device: 3 Cs - clear cytoplasm, central nucleus, corners on the nuclear membrane. | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Embryonal carcinoma]]. | |||
*Solid variant of [[yolk sac tumour]]. | |||
**Lacks fibrous septae and lymphocytes.<ref>URL: [http://webpathology.com/image.asp?case=34&n=8 http://webpathology.com/image.asp?case=34&n=8]. Accessed on: March 8, 2010.</ref> | |||
*[[Mixed germ cell tumour]]. | |||
*[[Choriocarcinoma]] - esp. if (multinucleated) syncytiotrophoblasts are present.<ref name=pmid157614>{{Cite journal | last1 = Hedinger | first1 = C. | last2 = von Hochstetter | first2 = AR. | last3 = Egloff | first3 = B. | title = Seminoma with syncytiotrophoblastic giant cells. A special form of seminoma. | journal = Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol | volume = 383 | issue = 1 | pages = 59-67 | month = Jul | year = 1979 | doi = | PMID = 157614 }}</ref> | |||
*Granulomatous orchitis - if [[granuloma]]s are present. | |||
====Images==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Seminoma_high_mag.jpg |Seminoma - high mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Seminoma_intermed_mag.jpg |Seminoma - intermed. mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Rete_testis_with_seminoma.jpg |Seminoma in the rete testis. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Seminoma_with_syncytiotrophoblasts_-_intermed_mag.jpg |Seminoma with syncytiotrophoblasts - intermed. mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Seminoma_with_syncytiotrophoblasts_-_very_high_mag.jpg |Seminoma with syncytiotrophoblasts - very high mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
</gallery> | |||
===IHC=== | |||
*D2-40 +ve ~100% of cases.<ref name=pmid17277761>{{Cite journal | last1 = Lau | first1 = SK. | last2 = Weiss | first2 = LM. | last3 = Chu | first3 = PG. | title = D2-40 immunohistochemistry in the differential diagnosis of seminoma and embryonal carcinoma: a comparative immunohistochemical study with KIT (CD117) and CD30. | journal = Mod Pathol | volume = 20 | issue = 3 | pages = 320-5 | month = Mar | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1038/modpathol.3800749 | PMID = 17277761 }}</ref> | |||
*CD117 +ve (ckit) ~92% of cases.<ref name=pmid17277761/> | |||
*CD30 -ve.<ref name=pmid16867864>{{Cite journal | last1 = Cossu-Rocca | first1 = P. | last2 = Jones | first2 = TD. | last3 = Roth | first3 = LM. | last4 = Eble | first4 = JN. | last5 = Zheng | first5 = W. | last6 = Karim | first6 = FW. | last7 = Cheng | first7 = L. | title = Cytokeratin and CD30 expression in dysgerminoma. | journal = Hum Pathol | volume = 37 | issue = 8 | pages = 1015-21 | month = Aug | year = 2006 | doi = 10.1016/j.humpath.2006.02.018 | PMID = 16867864 }}</ref> | |||
**Done to r/o [[embryonal carcinoma]]. | |||
*Cytokeratins usu. -ve, may have weak focal positivity.<ref name=pmid16867864/> | |||
*OCT3/4 +ve.<ref name=pmid20438407>{{Cite journal | last1 = Emerson | first1 = RE. | last2 = Ulbright | first2 = TM. | title = Intratubular germ cell neoplasia of the testis and its associated cancers: the use of novel biomarkers. | journal = Pathology | volume = 42 | issue = 4 | pages = 344-55 | month = Jun | year = 2010 | doi = 10.3109/00313021003767355 | PMID = 20438407 }}</ref> | |||
===Sign out=== | |||
<pre> | |||
RETROPERITONEAL SOFT TISSUE, RIGHT, CORE BIOPSY: | |||
- SEMINOMA. | |||
</pre> | |||
====Micro==== | |||
The sections show large atypical, discohesive cells with prominent nucleoli, central | |||
nuclei and moderate clear cytoplasm, intermixed with mature lymphocytes. Mitotic | |||
activity is present. | |||
====Small biopsy==== | |||
A mixed germ cell tumour cannot be excluded; given the small quantity of tumour, this | |||
biopsy is at a high risk for having undersampled other tumour components should they be | |||
present. Correlation with serology and consideration of re-biopsy is suggested. | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Testis]]. | |||
*[[Genitourinary pathology]]. | |||
*[[Dysgerminoma]]. | |||
*[[Germinoma]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
Revision as of 11:30, 10 July 2013
{{ Infobox diagnosis | Name = Seminoma | Image = Seminoma_high_mag.jpg | Width = | Caption = Seminoma. H&E stain. | Micro = fried egg-like cells (clear or eosinophilic cytoplasm, central nucleus), lymphocytic infiltrate (common), +/-syncytiotrophoblasts (rare), +/-granulomas (uncommon) | Subtypes = | LMDDx = embryonal carcinoma, ITGCN, mixed germ cell tumour, granulomatous orchitis | Stains = | IHC = OCT3/4 +ve, PLAP +ve, D2-40 +ve, CD30 -ve | EM = | Molecular = | IF = | Gross = | Grossing = | Site = testis | Assdx = ITGCN | Syndromes = | Clinicalhx = | Signs = testicular mass, +/-retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy | Symptoms = | Prevalence = | Bloodwork = +/-beta-hCG elevated | Rads = | Endoscopy = | Prognosis = good | Other = | ClinDDx = other testicular tumours (germ cell tumours, [[lymphoma) }} Seminoma is a common testicular germ cell tumour.
It should not be confused with the unrelated tumour called spermatocytic seminoma.
General
- Male counterpart of the dysgerminoma, which arise in the ovary.
- Most common germ cell tumour of the testis.
Clinical:
- Elevated serum LDH.
- Normal serum alpha fetoprotein.
- Usually normal beta-hCG.
Note:
- Rarely, it may present a retroperitoneal mass.[1]
Epidemiology & etiology
- Arises from intratubular germ cell neoplasia (ITGCN).
Microsopic
Features:
- Cells with fried egg appearance - key feature:
- Clear cytoplasm.
- Central nucleus, with prominent nucleolus.
- Nucleus may have "corners", i.e. it is not round.
- +/-Lymphoctyes - interspersed (very common).
- +/-Syncytiotrophoblasts, AKA syncytiotrophoblastic giant cells (STGCs),[2] present in ~10-20% of seminoma.[3]
- Large + irregular, vesicular nuclei.
- Eosinophilic vacuolated cytoplasm (contains hCG).
- Syncytiotrophoblasts = closest to mom in normal chorionic villi - covers cytotrophoblast.[4]
- +/-Florid granulomatous reaction.
Memory device: 3 Cs - clear cytoplasm, central nucleus, corners on the nuclear membrane.
DDx:
- Embryonal carcinoma.
- Solid variant of yolk sac tumour.
- Lacks fibrous septae and lymphocytes.[5]
- Mixed germ cell tumour.
- Choriocarcinoma - esp. if (multinucleated) syncytiotrophoblasts are present.[6]
- Granulomatous orchitis - if granulomas are present.
Images
IHC
- D2-40 +ve ~100% of cases.[7]
- CD117 +ve (ckit) ~92% of cases.[7]
- CD30 -ve.[8]
- Done to r/o embryonal carcinoma.
- Cytokeratins usu. -ve, may have weak focal positivity.[8]
- OCT3/4 +ve.[9]
Sign out
RETROPERITONEAL SOFT TISSUE, RIGHT, CORE BIOPSY: - SEMINOMA.
Micro
The sections show large atypical, discohesive cells with prominent nucleoli, central nuclei and moderate clear cytoplasm, intermixed with mature lymphocytes. Mitotic activity is present.
Small biopsy
A mixed germ cell tumour cannot be excluded; given the small quantity of tumour, this biopsy is at a high risk for having undersampled other tumour components should they be present. Correlation with serology and consideration of re-biopsy is suggested.
See also
References
- ↑ Preda, O.; Nicolae, A.; Loghin, A.; Borda, A.; Nogales, FF. (2011). "Retroperitoneal seminoma as a first manifestation of a partially regressed (burnt-out) testicular germ cell tumor.". Rom J Morphol Embryol 52 (1): 193-6. PMID 21424055.
- ↑ Zhou, Ming; Magi-Galluzzi, Cristina (2006). Genitourinary Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 542. ISBN 978-0443066771.
- ↑ URL: http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?case=31&n=10. Accessed on: 22 May 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/45/Gray37.png. Accessed on: 31 May 2010.
- ↑ URL: http://webpathology.com/image.asp?case=34&n=8. Accessed on: March 8, 2010.
- ↑ Hedinger, C.; von Hochstetter, AR.; Egloff, B. (Jul 1979). "Seminoma with syncytiotrophoblastic giant cells. A special form of seminoma.". Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol 383 (1): 59-67. PMID 157614.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Lau, SK.; Weiss, LM.; Chu, PG. (Mar 2007). "D2-40 immunohistochemistry in the differential diagnosis of seminoma and embryonal carcinoma: a comparative immunohistochemical study with KIT (CD117) and CD30.". Mod Pathol 20 (3): 320-5. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800749. PMID 17277761.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Cossu-Rocca, P.; Jones, TD.; Roth, LM.; Eble, JN.; Zheng, W.; Karim, FW.; Cheng, L. (Aug 2006). "Cytokeratin and CD30 expression in dysgerminoma.". Hum Pathol 37 (8): 1015-21. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2006.02.018. PMID 16867864.
- ↑ Emerson, RE.; Ulbright, TM. (Jun 2010). "Intratubular germ cell neoplasia of the testis and its associated cancers: the use of novel biomarkers.". Pathology 42 (4): 344-55. doi:10.3109/00313021003767355. PMID 20438407.