Difference between revisions of "Gross pathology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (+image) |
(→Gross spot diagnosis: split out) |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
*[[Calcific aortic stenosis]]. | *[[Calcific aortic stenosis]]. | ||
==Gross spot | ==Gross pathology spot diagnoses== | ||
{{Main|Gross pathology spot diagnoses}} | |||
== | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 17:22, 27 July 2014

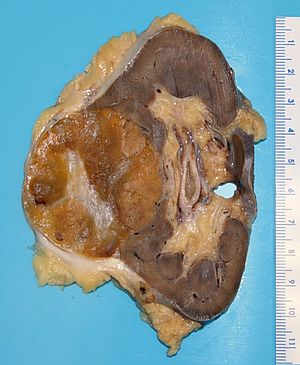
A kidney tumour (renal oncocytoma) at the time of grossing.
Gross pathology, also simply gross, refers to the macroscopic pathology, and the macroscopic assessment of pathology specimens. It may include preparation of tissue for a microscopic examination. It is an essential part of pathologic assessments.
The process of cutting up specimens is known as grossing (North American term), cut-up or macroscopic cut-up (Australian term).
Specimen opening
- Usually referred to simply as opening.
- May go by the term freshing.
- The first part of a gross pathologic assessment.
Components
- Orient the specimen.
- Paint with ink - if applicable.
- A good general rule is: ink before you think.
- Cut open for fixation - if not immediately blocked.
Gross only
Which specimens are "gross only" typically depends on institutional policy.[1]
Common gross only specimens
- Teeth.
- Foreign bodies.
- Femoral head with osteoarthritis - no fracture & no history of cancer.
- Calcific aortic stenosis.
Gross pathology spot diagnoses
Main article: Gross pathology spot diagnoses
See also
- Basics.
- EIT.
- Tissue loss.
References
- ↑ Zarbo, RJ.; Nakhleh, RE. (Feb 1999). "Surgical pathology specimens for gross examination only and exempt from submission: a College of American Pathologists Q-Probes study of current policies in 413 institutions.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 123 (2): 133-9. doi:10.1043/0003-9985(1999)1230133:SPSFGE2.0.CO;2. PMID 10050786.