Hyperplastic polyp
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Hyperplastic polyp | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
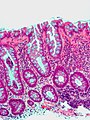
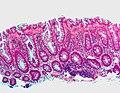
 Hyperplastic polyp. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | serrated architecture without glandular abnormalities |
| Subtypes | microvesicular serrated polyps (MVSPs), goblet cell serrated polyps (GCSPs). |
| LM DDx | sessile serrated adenoma - see gastrointestinal polyps |
| Gross | usually rectum or sigmoid, typically < 5mm |
| Site | colon, rectum |
|
| |
| Syndromes | hyperplastic polyposis syndrome |
|
| |
| Symptoms | asymptomatic |
| Prevalence | very common |
| Endoscopy | pedunculated or sessile |
| Prognosis | good |
| Clin. DDx | normal colon, sessile serrated adenoma |
- The stomach lesion is dealt with in hyperplastic polyp of the stomach.
The hyperplastic polyp of the colon and rectum is a very common. It is commonly abbreviated HP.
General
- Most common type of polyp:
- Approximately 90% of all colonic polyps.[1]
- May be part of hyperplastic polyposis syndrome.[2]
Gross
Features:[3]
- Flat lesion, usually <= 5mm.
- Typically in the distal large bowel (rectum, sigmoid colon).
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Irregular crypt architecture - tortuosity.
- Serrated epithelial cells (at the surface of the gland) - only colorectal polyps - key feature.
- Serrated appearance = saw-tooth appearance, epithelium has jagged edge.
Notes:
- Significant negatives:
- No nuclear atypia; glands darker staining deep... lighter staining luminal.
- In the colon goblet cells should be present (as is usual).
- Inflammation -- cryptitis or even crypt abscesses -- is considered to arise due to trauma.[citation needed]
- It is usually not reported.
DDx:
Images
www:
Subclassification
- Usually not subclassified as there is no demonstrated prognostic significance;[2] the subtyping is an academic exercise.
HPs may be subclassified into two groups:[2]
- Microvesicular serrated polyps (MVSPs).
- Goblet cell serrated polyps (GCSPs).
Features of the HP subtypes:[2]
| Subtype | Histology | Mutations | Clinical relevance |
| Microvesicular | microvesicles at the surface, serration at the surface to the mid portion of glands |
BRAF V600E, CIMP | possible sessile serrated adenoma precursor |
| Goblet cell | superficial goblet cells, serration at the surface |
KRAS | unknown; probably benign |
Notes:
- CIMP = CpG island methylation phenotype.
Sign out
COLONIC POLYP, 35 CM, BIOPSY: - HYPERPLASTIC POLYP.
COLONIC POLYP, SIGMOID COLON, BIOPSY: - HYPERPLASTIC POLYP.
POLYP, RECTUM, BIOPSY: - HYPERPLASTIC POLYP.
Numerous hyperplastic polyps
COLONIC POLYP(S), BIOPSY: - HYPERPLASTIC POLYP, SEE COMMENT. COMMENT: Eight pieces of tissue were received. On microscopy eight pieces of tissue are identified and all eight (individually) have the diagnostic features of a hyperplastic polyp. If these fragments all represent individual polyps and more polyps of this type are present in the individual, it raises the possibility of a serrated polyposis syndrome.
Micro
Goblet cell type
The sections show colonic-type mucosa with superficial serrations rich in goblet cells. There are no serrations in the crypt base and there is no crypt base dilation. No dysplasia is present.
Generic
The sections show colonic-type mucosa with superficial serrations. There are no serrations in the crypt base and there is no crypt base dilation. No dysplasia is present.
See also
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 858. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Huang, CS.; Farraye, FA.; Yang, S.; O'Brien, MJ. (Feb 2011). "The clinical significance of serrated polyps.". Am J Gastroenterol 106 (2): 229-40; quiz 241. doi:10.1038/ajg.2010.429. PMID 21045813.
- ↑ Rex, DK.; Ahnen, DJ.; Baron, JA.; Batts, KP.; Burke, CA.; Burt, RW.; Goldblum, JR.; Guillem, JG. et al. (Sep 2012). "Serrated lesions of the colorectum: review and recommendations from an expert panel.". Am J Gastroenterol 107 (9): 1315-29; quiz 1314, 1330. doi:10.1038/ajg.2012.161. PMID 22710576.