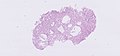
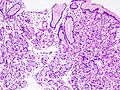
Fundic gland polyp
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Fundic gland polyp | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
| LM DDx | hyperplastic polyp of the stomach |
| Site | stomach - usually fundus |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | gastroesophageal reflux disease - thus PPI use |
| Syndromes | familial adenomatous polyposis |
|
| |
| Prevalence | common |
| Endoscopy | polyps |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | gastric adenoma, hyperplastic polyp of the stomach |
Fundic gland polyp, abbreviated FGP, is a relatively common pathology of the stomach. It is associated with familial adenomatous polyposis and proton pump inhibitor use.
General
Clinical significance
- Weak association with FAP (familial adenomatous polyposis).[1][2]
- Associated with chronic proton pump inhibitors (PPI) use -- approximately 4x risk.[3]
Notes:
- Animal studies suggested PPIs cause neuroendocrine tumours -- but this has not been found in humans.[4]
Gross
- Polyps.
Image:
Microscopic
Features:[5]
- Polypoid shape (may not be appreciated on microscopy).
- Dilated gastric glands.
- Flatted epithelial lining (consisting of normal foveolar epithelium) - key feature.
Notes:
- The presence of dysplastic changes should prompt consideration of FAP.
DDx:
- Hyperplastic polyp of the stomach - has foveolar hyperplasia, gland dilation may be present.
Images
www:
Sign out
POLYP, STOMACH, BIOPSY: - FUNDIC GLAND POLYP. - NEGATIVE FOR INTESTINAL METAPLASIA. - NEGATIVE FOR HELICOBACTER-LIKE ORGANISMS. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Spiegel, A.; Stein, P.; Patel, M.; Patel, R.; Lebovics, E. (Jan 2010). "A report of gastric fundic gland polyps.". Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y) 6 (1): 45-8. PMID 20567540.
- ↑ Freeman HJ (March 2008). "Proton pump inhibitors and an emerging epidemic of gastric fundic gland polyposis". World J. Gastroenterol. 14 (9): 1318-20. PMID 18322941. http://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/14/1318.asp.
- ↑ Jalving M, Koornstra JJ, Wesseling J, Boezen HM, DE Jong S, Kleibeuker JH (November 2006). "Increased risk of fundic gland polyps during long-term proton pump inhibitor therapy". Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 24 (9): 1341-8. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.03127.x. PMID 17059515.
- ↑ Masaoka T, Suzuki H, Hibi T (May 2008). "Gastric epithelial cell modality and proton pump inhibitor". J Clin Biochem Nutr 42 (3): 191-6. doi:10.3164/jcbn.2008028. PMC 2386521. PMID 18545640. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2386521/.
- ↑ URL: http://moon.ouhsc.edu/kfung/jty1/opaq/PathQuiz/A2B001-PQ01-M.htm. Accessed on: 19 October 2010.