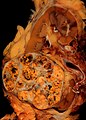
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma
| Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 Clear cell renal cell carcinoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | solid or trabecular pattern, polygonal cells usually with clear cytoplasm, central nucleus, delicate branching vasculature (chicken wire-like), +/-hyaline bodies |
| Subtypes | classic, eosinophilic variant |
| LM DDx | chromophobe renal cell carcinoma, clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma, Xp11.2 translocation carcinoma, adrenocortical carcinoma, alveolar soft part sarcoma |
| Stains | Hale's colloidal iron stain -ve |
| IHC | CK7 -ve, CK20 -ve, TFE3 -ve |
| Site | kidney - see kidney tumours |
|
| |
| Syndromes | von Hippel-Lindau syndrome, familial clear cell renal cell carcinoma |
|
| |
| Signs | +/-hematuria, +/-abdominal mass |
| Prevalence | common |
| Radiology | renal mass |
| Prognosis | good-to-poor - dependent on stage and grade |
| Clin. DDx | other renal tumours |
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma, abbreviated CRCC or CCRCC, is the most common type of renal cell carcinoma.
General
- Most common subtype of RCC.
- May be associated with Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome.
- Familial clear cell renal cell carcinoma[1] - usually VHL gene mutation.[2]
- VHL gene not mutated in all cases.[3]
Gross
- Gold/yellow.
- +/-Haemorrhage (common).
- +/-Necrosis (common in large tumours).
- +/-Calcification.
- +/-Cysts.
Image
Microscopic
Features:[4]
- Solid or trabecular pattern.
- Polygonal cells.
- Clear cytoplasm.
- Central nucleus.
- Delicate branching vasculature.
- Often called "chicken wire-like" vasculature.
- +/-Rhabdoid cells:
- Eccentric nucleus.
- Abundant eosinophilic cytoplasma.
Notes:
- Cytoplasm may be eosinophilic.[5]
- This change is typically focal - other areas have a classic appearance.
- Chicken wire-like vasculature present - helps distinguish from other tumours.
- Hyaline bodies common.[6]
- Not common in papillary RCC.
- Clear cytoplasm - due to lipid content.
DDx:
- Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma.
- Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma.
- Xp11.2 translocation carcinoma.
- Adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC)
- EMA -ve, CKs mostly -ve, inhibin +ve (neg. in RCC).[7]
- Alveolar soft part sarcoma.
- Adrenal gland, normal.
- Epithelioid angiomyolipoma.
Images
Stains
- Hale's colloidal iron -ve.
- +ve in chromophobe RCC.
Note: Hale's colloidal iron does not stain iron... it stains hemosiderin.[8]
Clear cell vs. chromophobe:
- Chromophobe: "translucent" (NOT quite clear), reticulated, Hale's colloidal iron stain+, CK7+ (cell membrane).
IHC
- CD10 +ve.
- Vimentin +ve.
- CK7 -ve.
- CK20 -ve.
CCRCC versus chromophobe RCC
ISUP recommends:[9]
- CD117 -ve (+ve in ChRCC).
- CAIX (carbonic anhydrase CA IX) +ve (membranous).[10]
- CK7 -ve (+ve in ChRCC).
Another set of stains:[11]
- Vimentin +ve.
- -ve in ChRCC.
- CD117 -ve.
- +ve ~80% of ChRCC.
CCRCC versus CCPRCC
- CAIX +ve (strong membranous).
- CK7 -ve.
- AMACR -ve.
Others:
- CD10 +ve.
- Usually -ve in clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma.
CCRCC versus Xp11.2 translocation carcinomas
ISUP recommends:[9]
- Cathepsin K -ve.[12]
- TFE3 -ve.
- TFEB -ve.
Sign out
Biopsy
Kidney Mass, Left, Core Biopsy: - CLEAR CELL RENAL CELL CARCINOMA, preliminary nucleolar grade 2 (see comment) - No renal parenchyma identified Comment: The quantity of tissue at microscopy is limited, and may not be representative of the lesion identified radiologically.
Resection
Note:
- The surgeon wants the diagnosis and margin status; thus, these are included in the diagnosis line with the tumour stage.
KIDNEY, LEFT, NEPHRECTOMY: - CLEAR CELL RENAL CELL CARCINOMA, FUHRMAN GRADE 2, pT1a, pNx. -- MARGINS NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. -- PLEASE SEE TUMOUR SUMMARY.
Adrenal gland present
KIDNEY, RIGHT, RADICAL NEPHRECTOMY: - CLEAR CELL RENAL CELL CARCINOMA, FUHRMAN GRADE 2, pT1a, pNx. -- MARGINS NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. -- PLEASE SEE TUMOUR SUMMARY. - ADRENAL GLAND WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS.
KIDNEY, RIGHT, RADICAL NEPHRECTOMY: - CLEAR CELL RENAL CELL CARCINOMA, FUHRMAN GRADE 3, pT1b, pNx. -- MARGINS NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. -- PLEASE SEE TUMOUR SUMMARY. - ADRENAL GLAND WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS.
Micro
The sections show a tumour with a chicken wire-like vasculature composed of clear cells with basally stratified nuclei. Hemosiderin-laden macrophages are present. Necrosis is present. Abundant hyaline globules are present.
There is no perinuclear clearing. The cytoplasm is not whispy. Collections of macrophages are not identified within the stroma of the tumour. Papillae are not evident.
Rare, small nucleoli are visible with the 10x objective. The tumour nuclei are approximately 15 micrometers.
Alternate
The sections show cohesive mildly atypical clear cells with a columnar morphology. Small cystic spaces are present. The nuclei are basal stratified. Nucleoli are not prominent. Siderophages are present. Blood is present.
No perinuclear halos are apparent. No papillary structures are identified. No definite renal parenchyma is seen.
See also
References
- ↑ Keefe, SM.; Nathanson, KL.; Rathmell, WK. (Aug 2013). "The molecular biology of renal cell carcinoma.". Semin Oncol 40 (4): 421-8. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2013.05.006. PMID 23972705.
- ↑ Foster, RE.; Abdulrahman, M.; Morris, MR.; Prigmore, E.; Gribble, S.; Ng, B.; Gentle, D.; Ready, S. et al. (Apr 2007). "Characterization of a 3;6 translocation associated with renal cell carcinoma.". Genes Chromosomes Cancer 46 (4): 311-7. doi:10.1002/gcc.20403. PMID 17205537.
- ↑ Woodward, ER.; Clifford, SC.; Astuti, D.; Affara, NA.; Maher, ER. (May 2000). "Familial clear cell renal cell carcinoma (FCRC): clinical features and mutation analysis of the VHL, MET, and CUL2 candidate genes.". J Med Genet 37 (5): 348-53. PMID 10807693.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1017-8. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 291. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ AFIP Renal Tumours Book.
- ↑ Zhou, Ming; Magi-Galluzzi, Cristina (2006). Genitourinary Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 285. ISBN 978-0443066771.
- ↑ Latta. 27 January 2009.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Amin MB, Epstein JI, Ulbright TM, et al. (August 2014). "Best practices recommendations in the application of immunohistochemistry in urologic pathology: report from the international society of urological pathology consensus conference". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 38 (8): 1017–22. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000254. PMID 25025364.
- ↑ Al-Ahmadie HA, Alden D, Fine SW, et al. (July 2011). "Role of immunohistochemistry in the evaluation of needle core biopsies in adult renal cortical tumors: an ex vivo study". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 35 (7): 949–61. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31821e25cd. PMID 21677535.
- ↑ Liu, L.; Qian, J.; Singh, H.; Meiers, I.; Zhou, X.; Bostwick, DG. (Aug 2007). "Immunohistochemical analysis of chromophobe renal cell carcinoma, renal oncocytoma, and clear cell carcinoma: an optimal and practical panel for differential diagnosis.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 131 (8): 1290-7. doi:10.1043/1543-2165(2007)131[1290:IAOCRC]2.0.CO;2. PMID 17683191.
- ↑ Martignoni G, Gobbo S, Camparo P, et al. (October 2011). "Differential expression of cathepsin K in neoplasms harboring TFE3 gene fusions". Mod. Pathol. 24 (10): 1313–9. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2011.93. PMID 21602817.