Hepatitis B
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Hepatitis B is a relatively common medical liver disease caused by the hepatitis B virus.
General
- May lead to hepatocellular carcinoma without cirrhosis.
- High prevalence.
- Diagnosis is by serology - details of serologic testing are in the medical liver disease article.
- A vaccination is available and done routinely in a many jurisdictions.[1]
Associated pathology:
Microscopic
Features:
- Lobular inflammation - this is non-specific finding.
- Hepatocyte necrosis:
- Necrotic hepatocytes look a lot like neutrophils - however:
- Cytoplasm is more pink.
- Round apoptotic bodies.
- Necrotic hepatocytes look a lot like neutrophils - however:
- Hepatocyte necrosis:
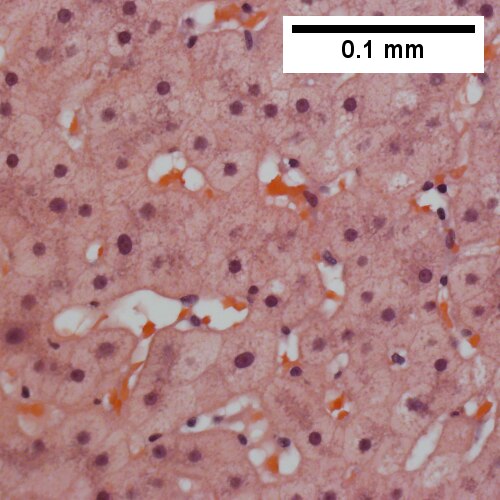
- Ground glass hepatocytes - important.
DDx:
Image






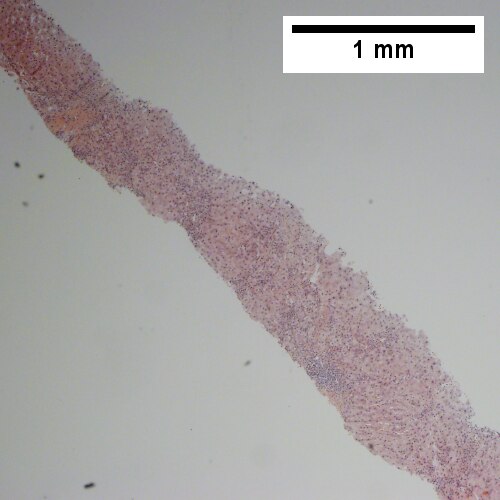
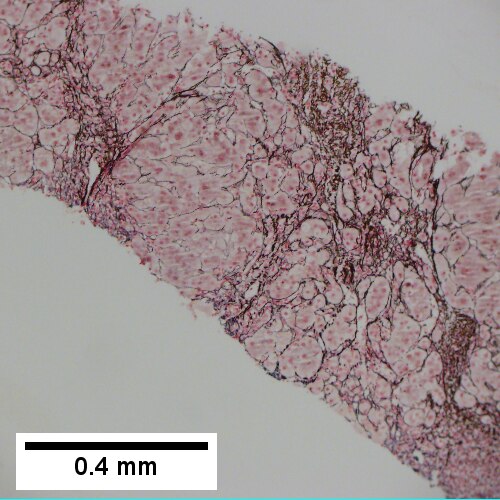
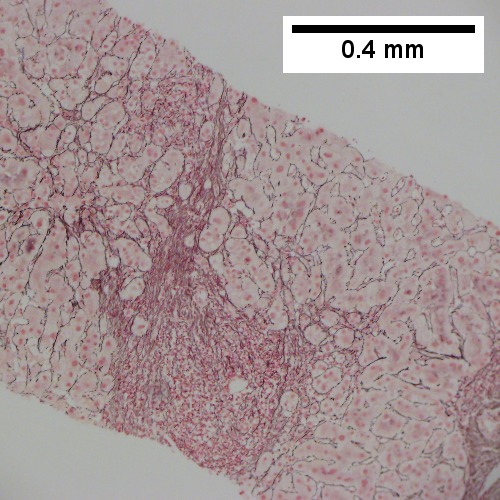
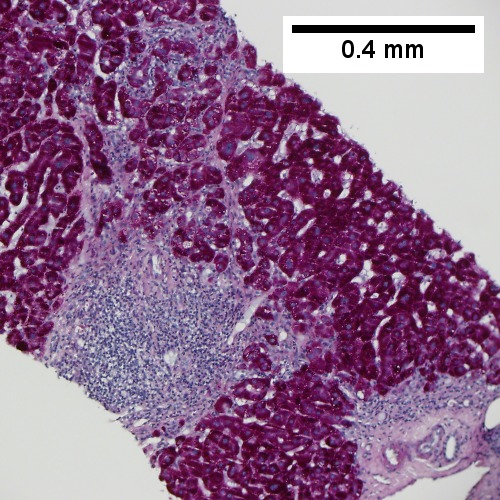
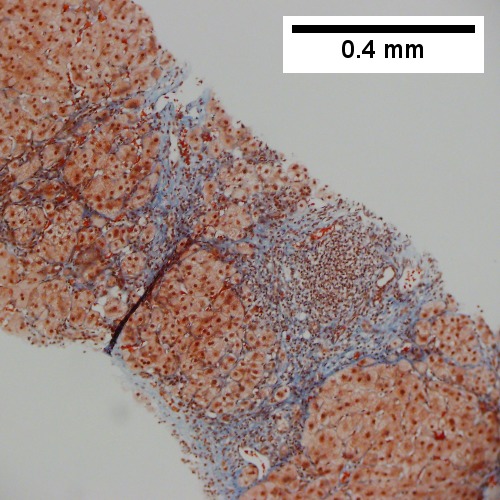
Hepatitis B. Metavir activity index 3. Piecemeal necrosis 2. Lobular necrosis 2. Fibrosis stage 3. Portal triads, expanded, inflamed and without sharp edges. Inflammation amid hepatocytes. (TL 40X). Reticulin with bridging necrosis (TR 100X). Reticulin with extensive piecemeal necrosis (ML 100X). PAS without diastase with extensive piecemeal necrosis (MR 100X). Trichrome with bridging, no nodules or extensive bridging on slides as a whole (BL 100X). Ground glass hepatocytes (BR 400X).
IHC
- Hepatitis B +ve.
See also
References
- ↑ Leuridan, E.; Van Damme, P. (Jul 2011). "Hepatitis B and the need for a booster dose.". Clin Infect Dis 53 (1): 68-75. doi:10.1093/cid/cir270. PMID 21653306.
