Tuberous sclerosis
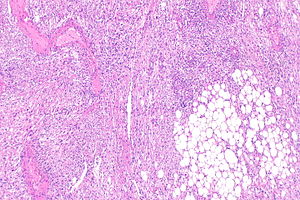
Micrograph showing a renal angiomyolipoma, as may be seen in tuberous sclerosis. H&E stain. (WC/KGH)
Tuberous sclerosis, also tuberous sclerosis complex (abbreviated TSC), is an autosomal dominant syndrome associated with an increased risk of hamartomas and some risk increase for malignant tumours.
Historically described as:[1]
- Epilepsy.
- Mental retardation.
- Adenoma sebaceum (angiofibromas).
Diagnostic consensus criteria published (2012, OpenAcess).
Also called Bourneville-Pringle disease.
General
- Autosomal dominant with variable penetrance.[2]
- Majority (60-70%) are de novo mutations.[2]
- May be treated with a mTOR inhibitor, e.g. everolimus.[3]
Associations
Pathologic:
- Renal angiomyolipoma.
- Cardiac rhabdomyoma.
- Lymphangiomyomatosis.
- Seen in ~1/3 of females with TSC in one series.[4]
- Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA).[5]
- Usu at. thalamo-striatal sulcus of the lateral ventricle.
- Contrast enhancement and progressive growth.
- Precursor: Subependymal nodules (SENs) without enhancement.
- Renal cysts.[2]
- Seen in ~45% of individuals with TSC in one series, no gender bias.[4]
- Tuberous sclerosis-associated renal cell carcinoma - an evolving entity.[2]
- Multifocal micronodular pneumocyte hyperplasia[6] - may mimic atypical adenomatous hyperplasia.[7]
- Cortical tubers (malformative, epilepsy-associated).[8]
- Seen in 80-90% of the cases.
- Gyrus is usu. thickened, raised, and occasionally dimpled.
- Giant cells, dysmorphic neurons, disrupted cortical lamination, gliosis, calcifications.
- Ballon cells are Vim+ve, MAP2+ve, Nestin+ve, GFAP+/-ve, NeuN+/-ve.
- TSC2 has larger and more numerous tubers.[9]
- DD: Focal cortical dysplasia ILAE type IIB (Tubers are usu. multifocal).
Note:
- The same genes (TSC1, TSC2) are implicated in PEComas.
- Renal lesions are seen in ~60% of patients.[4]
- Scheme illustrates types of neuropathologic changes in tuberous sclerosis complex. 1- isolated balloon cells in white matter, TSC-/-; 2- heterotopic cluster with dysplastic neurons TSC-/+; 3- subependymal nodules and 4- subependymal giant cell astrocytoma in ependyma of third ventricle (note that this is not usual localisation for both lesions, which is rather ependyma of lateral ventricles) 5- cortical tuber; 6 - linear migration streak. This scheme is based on DiMario, F Brain abnormalities in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex J Child Neurol, 9, 650-657. 2004.[10]
Mnemonic SALSA HEART:[11]
- Shagreen patches.
- Shagreen patch = connective-tissue nevus composed of collagen, i.e. collagenoma.[12]
- Ash-leaf spots.
- Lymphangioleiomyomatosis.
- SEGA.
- Angiofibroma.
- Hamartomas.
- Epilepsy.
- Angiomyolipoma.
- Rhabdomyoma.
- Tubers.
Genes
Notes:
- The proteins (hamartin and tuberin) are expressed in a wide variety of tissues.[17]
Incidence
~1 in 10,000 population.[1][16]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1177711-overview. Accessed on: 13 February 2011.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Guo, J.; Tretiakova, MS.; Troxell, ML.; Osunkoya, AO.; Fadare, O.; Sangoi, AR.; Shen, SS.; Lopez-Beltran, A. et al. (Nov 2014). "Tuberous Sclerosis-associated Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Clinicopathologic Study of 57 Separate Carcinomas in 18 Patients.". Am J Surg Pathol 38 (11): 1457-67. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000248. PMID 25093518.
- ↑ Pirson, Y. (Jul 2013). "Tuberous sclerosis complex-associated kidney angiomyolipoma: from contemplation to action.". Nephrol Dial Transplant 28 (7): 1680-5. doi:10.1093/ndt/gft009. PMID 23413089.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Rakowski SK, Winterkorn EB, Paul E, Steele DJ, Halpern EF, Thiele EA (November 2006). "Renal manifestations of tuberous sclerosis complex: Incidence, prognosis, and predictive factors". Kidney Int. 70 (10): 1777–82. doi:10.1038/sj.ki.5001853. PMID 17003820.
- ↑ Grajkowska, W.; Kotulska, K.; Jurkiewicz, E.; Roszkowski, M.; Daszkiewicz, P.; Jóźwiak, S.; Matyja, E. (2011). "Subependymal giant cell astrocytomas with atypical histological features mimicking malignant gliomas.". Folia Neuropathol 49 (1): 39-46. PMID 21455842.
- ↑ Kobayashi, T.; Satoh, K.; Ohkawa, M. (Feb 2005). "Multifocal micronodular pneumocyte hyperplasia associated with tuberous sclerosis.". Acta Radiol 46 (1): 37-40. PMID 15841738.
- ↑ Kobashi, Y.; Sugiu, T.; Mouri, K.; Irei, T.; Nakata, M.; Oka, M. (Jun 2008). "Multifocal micronodular pneumocyte hyperplasia associated with tuberous sclerosis: differentiation from multiple atypical adenomatous hyperplasia.". Jpn J Clin Oncol 38 (6): 451-4. doi:10.1093/jjco/hyn042. PMID 18535095.
- ↑ Cotter, JA. (Apr 2019). "An update on the central nervous system manifestations of tuberous sclerosis complex.". Acta Neuropathol. doi:10.1007/s00401-019-02003-1. PMID 30976976.
- ↑ Overwater, IE.; Swenker, R.; van der Ende, EL.; Hanemaayer, KB.; Hoogeveen-Westerveld, M.; van Eeghen, AM.; Lequin, MH.; van den Ouweland, AM. et al. (12 2016). "Genotype and brain pathology phenotype in children with tuberous sclerosis complex.". Eur J Hum Genet 24 (12): 1688-1695. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2016.85. PMID 27406250.
- ↑ DiMario, FJ. (Sep 2004). "Brain abnormalities in tuberous sclerosis complex.". J Child Neurol 19 (9): 650-7. doi:10.1177/08830738040190090401. PMID 15563010.
- ↑ URL: http://www.usmle-forums.com/usmle-step-1-mnemonics/303-tuberous-sclerosis.html. Accessed on: 20 October 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://dermatology-s10.cdlib.org/1611/articles/3_2009-11-17/batra.html. Accessed on: 18 February 2012.
- ↑ Jindal, R.; Jain, A.; Gupta, A.; Shirazi, N. (Jun 2013). "Ash-leaf spots or naevus depigmentosus: a diagnostic challenge.". BMJ Case Rep 2013. doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-007008. PMID 23761491.
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 605284
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 191092
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Al-Saleem T, Wessner LL, Scheithauer BW, et al. (November 1998). "Malignant tumors of the kidney, brain, and soft tissues in children and young adults with the tuberous sclerosis complex". Cancer 83 (10): 2208–16. PMID 9827727.
- ↑ Johnson, MW.; Kerfoot, C.; Bushnell, T.; Li, M.; Vinters, HV. (Mar 2001). "Hamartin and tuberin expression in human tissues.". Mod Pathol 14 (3): 202-10. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3880286. PMID 11266527.
